GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupGEOGRAPHY P1
GRADE 12
JUNE 2016
MEMORANDUM
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
SECTION A:
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY: CLIMATE AND WEATHER AND GEOMORPHOLOGY
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 Isobars ✓
1.1.2 1020 hectopascals / millibars ✓
1.1.3 South Atlantic High / St Helena High ✓
1.1.4 South west ✓
1.1.5 Coastal low ✓
1.1.6 Berg winds ✓
1.1.7 Winter ✓
1.1.8 The westerly wind belt ✓ (8 x 1)
(8)
1.2
1.2.1 Interfluve ✓
1.2.2 Source ✓
1.2.3 Mouth ✓
1.2.4 Drainage basin ✓
1.2.5 Watershed ✓
1.2.6 Confluence ✓
1.2.7 Upper course (7 x 1)
(7)
1.3
1.3.1
- Cumulus clouds ✓(1 x 1) (1)
- Any Cirrus clouds ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
1.3.2
- Increase of air movement in one of the air masses (westerly or polar winds) ✓
- Disturbance in the westerly wind belt ✓
- Shape of coastal lines ✓
- Mountain ranges ✓
- Contrasts between sea- and land temperatures ✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 1)
(2)
1.3.3 Air is warmer in X, therefore have to rise higher to cool-off and reach freezing point. ✓✓
OR
Air is colder/cooler at Y, therefore reaching freezing point at a lower height than at X, where the temperature is warmer. ✓✓
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
1.3.4 Cumulonimbus clouds are formed when cold dense air causes a rapid uplift of warmer lighter air. ✓✓
Nimbostratus clouds forms when warm air moves /rises very slowly over colder denser air ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
1.3.5 Cold air holds less moisture than warm air✓✓
As the system moves in a easterly direction, the dew point temperature will increase around the warm front✓✓ and decrease around the cold front✓✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.4
1.4.1 Sub-tropical high ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
1.4.2 A moves over cold waters, therefore heavy and dense, and forces the warmer air of B, which originates in warm waters, to rise. ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
1.4.3
- Cumulonimbus ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
- Convection rain ✓ / Thunderstorms✓/ Heavy Rainfall ✓
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1) - D ✓
Line thunderstorms develop to the east of the moisture front due to uplift from colder air from the west. ✓✓ (1 + 2) (3) - Negative impact
- Heavy rainfall will cause flooding ✓✓
- Lightning may cause veldfires destroying crops ✓✓
- Lightning may strike animals and cause death ✓✓
- Can cause soil erosion which will influence productivity of the soil in the long run ✓✓
Positive impact - Rainfall will fill dams for irrigation purposes ✓✓
- After flooding the soil will be naturally fertilised due to silt deposits ✓✓
- Ground water will be revived ✓✓
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
1.5
1.5.1
- Windgap ✓
- Elbow of capture ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
1.5.2 Dry river channel ✓
River gravel can be found ✓
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
1.5.3 Will cause incised/entrenched meanders. ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
1.5.4
- X is more energetic and flows over less resistant rocks. ✓✓
- X flows from a steeper gradient, causing headward erosion in the watershed. ✓✓
- X has more volume of water due to higher rainfall in the catchment area ✓✓
[NOTE: Candidates may also refer to Y and suggest reasons why it was possible to capture Y]
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.5.5
- Less water will be available, so farmers have to channel water from elsewhere. ✓✓
- Farming will become more expensive as new infrastructure have to be constructed.✓✓
- Productivity will decrease as water become less. ✓✓
- Industries will have to transport more water at higher costs, therefore increasing the selling price of products. ✓✓
(Any THREE) (3 x 2) (6)
1.6
1.6.1 P Cross profile ✓
Q Longitudinal profile ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
1.6.2 3 ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
1.6.3
- R Downward/Headward erosion ✓(1)
T Deposition ✓ (1 + 1) (2) - R Turbulent✓T
Laminar✓ (1 + 1) (2)
1.6.4
- Fast flowing energetic rivers will cut into the landscape in the upper course ✓✓
- Downward erosion dominant✓✓
- During the middle course the river starts to meander as lateral erosion dominates and this makes the area wider and more open✓✓
- All knickpoints like waterfalls, will be eroded away through headward and backward erosion✓✓
- In the lower course the river will deposit sediments, making the area more level. ✓✓
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[75]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Heat island ✓
2.1.2 3,3 °C ✓
2.1.3 Buildings✓ / Commercial activities (Any ONE)
2.1.4 X ✓
2.1.5 Y ✓
2.1.6 Greenwalls, roofs and parkland ✓
Green areas / Plants ✓
(Any ONE)
2.1.7 Convection currents ✓ (7 x 1)
(7)
2.2
2.2.1 B ✓
2.2.2 F ✓
2.2.3 E ✓
2.2.4 A ✓
2.2.5 D ✓
2.2.6 A ✓
2.2.7 B ✓
2.2.8 D ✓ (8 x 1) (8)
2.3
2.3.1 4 ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.2 July ✓
August ✓
September ✓
(Any ONE) (1 x 1)
(1)
2.3.3 West Northwest ✓
The direction is driven by the tropical easterlies ✓✓ (1 + 2) (3)
2.3.4 Coriolis force is a prerequisite for the development of tropical cyclones and in the area on the map, the coriolis force is zero or below 5 degrees. ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
2.3.5 San Juan
The storm will be in its initial or immature stage ✓✓
Only light rain and drizzle occur now ✓✓
The area being influenced by the storm is still small ✓✓
Miami
Storm will have developed into its mature stage ✓✓
Gale force winds and heavy rainfall occur ✓✓
Storm causing huge waves, which may damage the harbour region ✓✓
Low lying areas in Miami will flood due to amount of rainfall ✓✓
Area that is being influenced is at its maximum, approximately 500 km from the eye (centre) ✓✓
Developed and developing nations
San Juan is a developing country and therefore the majority of building structures and infrastructure will be in a poorer condition than those of Miami ✓✓
The warning systems of Miami will be more efficient and quicker than those of San Juan causing more life losses at San Juan ✓✓
San Juan has poorer security and emergency services to deal with the effects of the tropical cyclone ✓✓
Miami has more financial assistance from the USA government to deal with the effects of the tropical cyclone, while San Juan will have to rely mostly on international assistance✓✓
(NOTE – First argument about the stages of development must NOT be mixed with the second argument of level of development of the countries.)
(Any FOUR – Accept other relevant responses) (4 x 2)
2.4
2.4.1 Microclimate is the climate in a small area that is different from the area surrounding it. ✓
(CONCEPT) (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.2 Northern Hemisphere ✓
South facing slope has the highest average temperature ✓✓ (1 + 2) (3)
2.4.3 Katabatic winds✓ / Gravitational winds✓ / Mountain breeze✓
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.4 Apples trees are more frost resistant than peach trees. ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
2.4.5
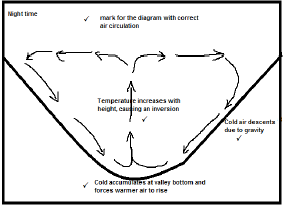
2.4.6 Upslope or anabatic winds blows up the mountain ✓✓
This movement of air takes the polluted air away from the surface and higher up into the atmosphere, thus ‘cleaning’ the air ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
2.5
2.5.1
- Oxbow lake ✓
- Meander scar ✓ (1 + 1) (2)
2.5.2 Recurring erosion at the undercut slope and deposition at the slip-off slope. ✓✓
Eventually the stream will cut through the neck of the meander and separate it from the stream. ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
2.5.3 Continuous overflowing of the river causing deposition of sediments or silt on the banks ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
2.5.4
- Soil is fertile and produce high yields per hectare ✓✓
- Enough water available, also for irrigation ✓✓
- Area is level, so building of infrastructure like transport and electricity facilities is easy and cheaper ✓✓
- Level area makes mechanisation easy ✓✓
- Continuous deposition of sediments keeps the plain naturally fertile ✓✓
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2)
(8)
2.6
2.6.1 When excess rain water, melted water or other sources of water flow over the earth’s surface. ✓
(CONCEPT) (1 x 1) (1)
2.6.2 Infiltration✓ (1 x 1) (1)
2.6.3 Through flow✓ (1 x 1) (1)
2.6.4
- The area at C experiences heavier rainfall causing more runoff ✓✓
- The slope at C is steeper. ✓✓
- There are more building structures at C than at B. ✓✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 2)
(4)
2.6.5
- More silt will be deposited in the river due to overgrazing. ✓✓
- Run off from crop farming activities consists of pesticides which will kill aquatic life and make water toxic✓✓
- The process of eutrophication will increase which may cause a disturbance of the aquatic food chain✓✓ (3 x 2)
(6)
[75]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Rural hamlet ✓
3.1.2 Land redistribution ✓
3.1.3 Basic need philosophy ✓
3.1.4 Rural ✓
3.1.5 Push forces ✓
3.1.6 Site ✓
3.1.7 Dispersed✓
3.1.8 Subsistence farming (8 x 1)
(8)
3.2
3.2.1 D (Centripetal forces) ✓
3.2.2 G (Hierarchy)✓
3.2.3 A (Sphere of influence)✓
3.2.4 F (Range)✓
3.2.5 H (Level of urbanisation)✓
3.2.6 C (Urban sprawl)✓
3.2.7 E (Urban decay)✓ (7 x 1)
(7)
3.3
3.3.1
- Fertile soil ✓
- Availability of fresh drinking water at the river ✓
- Building material✓
- Pasturage ✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 1)
(2)
3.3.2 A is dispersed✓
B is nucleated ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
3.3.3
- Large tracks of open fertile land ✓✓
- Close proximity of roads ✓✓
- Town market provide a market for products to be sold ✓✓
- Raw materials can be sent for processing to the New Industry ✓✓
- Flat land makes mechanisation easy ✓✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 2)
(4)
3.3.4
Advantages of nucleated rural settlement patterns
Safe as community can protect each other ✓✓
Farmers need less capital as they are able to share implements ✓✓
All public services are in close proximity e.g. school, clinics, police stations, etc. ✓✓
Disadvantages of nucleated rural settlement patterns
All farmers have to agree on farming methods, no individual initiative ✓✓
Properties are fragmented or too small to use mechanisation extensively✓✓
If soil erosion or other disasters occur, everyone will be affected ✓✓
(Any FOUR – Both advantages and disadvantages must be discussed. Accept other reasonable responses) (4 x 2)
(8)
3.4
3.4.1 Rural-urban migration ✓ (1 x 1) (2)
3.4.2
- Droughts ✓
- Floods ✓
- Soil erosion ✓
- Natural disasters like earthquakes, mass movement, etc. ✓
- Heavy frost ✓
(Any ONE – Accept other answers) (1 x 1) (1)
3.4.3
- Resources like fertile soil are not being used for the economy ✓✓
- Lack of skilled labour as people moved away in search of employment ✓✓
- Small businesses are forced to close down because of less buying power and farmers choosing to buy in bulk in bigger cities ✓✓
- Ageing of the area as young people leave in search of a ‘better’ future ✓✓
- Cycle of stagnation and decline continue in rural area ✓✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 2)
(4)
3.4.4 During the present country side there is still a travelling distance between rural and urban settlements due to low population numbers in urban areas ✓✓
During the future country side, the urban areas has grown considerably and expanded, the border is now near to the rural areas ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
3.5
3.5.1 An increase of people living in urban areas rather than rural areas✓ (CONCEPT) (1 x 1) (1)
3.5.2 Urban areas are depicted before urbanisation as being spacious, due to a lower concentration of people. After urbanisation they are depicted as being densely concentrated. ✓✓
(Any relevant answer related to the sketch.) (1 x 2) (2)
3.5.3
- Fertile soil is being removed ✓✓
- Natural habitats of species are being removed ✓✓
- Biodiversity and ecosystems disturbed ✓✓
- Increase of the heat island affect due to artificial production of heat ✓✓
- Air pollution increase due to industrialisation ✓✓
- Increase in general pollution e.g. water, noise and environmental problems occur.
(Any TWO) (2 x 2)
(4)
3.5.4
- Greenbelts help with the controlling of the growth of built-up areas ✓✓
- It forms borders and prevents neighbouring towns from merging ✓✓
- It preserves the character of each town ✓✓
- Provide open spaces and recreation areas to urban dwellers ✓✓
- Increase biodiversity and aesthetic appeal ✓✓
- Reduces the heat island affect ✓✓
(Any FOUR – Accept other reasonable responses) (4 x 2)
(8)
3.6
3.6.1 Heavy industry ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
3.6.2
- Large and heavy products can be found ✓
- Large and heavy equipment are being used ✓
- It’s has high capital intensity ✓
- Employs a large number of people✓
- Make use of bulk transport facilities like trains and cargo ships ✓
- Produces excess air and noise pollution ✓ (2 x 1)
(2)
3.6.3 It will cause acid rain and corrode building structures ✓✓
Smoke stick to buildings causing urban decay ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
3.6.4
- Install filters on the chimneys, which catch most of the dust and pollutants before its released into the air ✓✓
- Factories can switch from the use of coal to natural gas or other environmentally friendly energy generators ✓✓
- Make the chimney stack higher than the inversion layer ✓✓
(Any TWO) (2 x 2)
(4)
3.6.5
- Heavy industries cause air and noise pollution ✓✓
- Space is restricted near to the CBD and heavy industries need space for expansion ✓✓
- Land values are very high near the CBD ✓✓ (2 x 2)
(4)
[75]
TOTAL: 225