AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Multiple-choice questions
1.1.1 A ✓✓
1.1.2 B ✓✓
1.1.3 C ✓✓
1.1.4 D ✓✓
1.1.5 C ✓✓
1.1.6 B ✓✓
1.1.7 B ✓✓
1.1.8 A ✓✓
1.1.9 A ✓✓
1.1.10 D ✓✓ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Matching items
1.2.1 C ✓✓
1.2.2 G ✓✓
1.2.3 D ✓✓
1.2.4 H ✓✓
1.2.5 I ✓✓
1.2.6 K ✓✓
1.2.7 J ✓✓
1.2.8 F ✓✓
1.2.9 E ✓✓
1.2.10 B ✓✓ (10 x 2) (20)
1.3 Correct agricultural term
1.3.1 Price setting/price ✓
1.3.2 Organogram ✓
1.3.3 Annual leave ✓
1.3.4 Turnover ✓
1.3.5 Marketing costs ✓
1.3.6 Production capital ✓
1.3.7 Invoice ✓
1.3.8 Logbook ✓
1.3.9 Human resources ✓
1.3.10 Crop rotation ✓ (10 x 1) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
2.1 2.1.1 Examination of a candidate and motivation
- Farm manager
Candidate A ✓
Has good qualifications and management skills ✓ (2) - Farm worker
Candidate B ✓
Is good in technical skills ✓ (2)
2.1.2 A candidate that would not work in the workshop
- Candidate A ✓ (1)
2.1.3 Unskilled worker
- No unskilled worker ✓
- Because both candidates are trained and have qualifications and certificates ✓ (2)
2.2.1 THREE fixed capital from the case study
- Borehole ✓
- Reservoir ✓
- Land ✓
- Small-stock housing ✓ (Any 3) (3)
2.2.2 THREE methods to improve the productivity of agricultural land
- Scientific farming methods/Intercropping ✓
- Irrigation system ✓
- Diversification ✓ (3)
2.2.3 One method to reduce risks in a small-scale agricultural enterprise
- Diversification✓
- The risks are spread to different enterprises ✓
OR - Irrigation ✓
- less dependence on rainfall and unpredictable climate ✓
OR - Scientific practices ✓
- More precise to measure inputs ✓ (2)
2.2.4 Advantages of organic farming
- Less pollution with chemicals ✓
- Protection of the natural predators ✓ (2)
2.3 2.3.1 Description of the carrying capacity
- Savannah: moderate ✓ (1)
- Forest: very low ✓ (1)
- Grassland: highest ✓ (1)
- Karoo: low ✓ (1)
- Fynbos: low ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Feeding value and management of sweet and sour-veld
- Sweet veld
- Feeding value stays the same throughout the year ✓
-
- If veld is well managed, animals can be kept on pastures throughout the year without extra feeding✓
- Longer grazing periods as grass retains it nutritional value ✓
- Less to no supplementation in winter✓ (Any 2) (2)
- Sour-veld
- Feeding value is high during spring and summer ✓
- Feeding values during winter months are very low ✓
- Management include supplementary feeds during the winter ✓
- Shorter grazing periods as older grass tends to lose its palatability. ✓
- Providing supplementary feeds and licks in winter. ✓ (Any 3) (3)
2.4 Whole enterprise planning phases in their correct sequence
- Data collection ✓
- Land utilization planning ✓
- Alternative and potential ✓
- Systems ✓
- Sustainability ✓
- Management ✓ (6)
2.5 2.5.1 The physical aspects of the farm set out by farm budget
- What to produce ✓
- How much to produce/total hectares used for production ✓
- Resources to be invested ✓ (3)
2.5.2 TWO basic elements of a budget
- Estimated income ✓
- Estimated costs ✓ (2)
2.5.3 The use of cash flow budget as a financial tool
- To monitor expenditure/Checking whether money is spent as planned ✓
- To avoid cash management problems/The budget shows whether income will be enough to pay for expenditures when they arise ✓
- To indicate when surplus funds become available ✓
- Indicate the spread of funds for new investments ✓
- Indicate that the farm will always have enough money to operate/Ensure no cash flow problems during off seasons ✓ (Any 4) (4)
2.6 TWO reasons for soil cultivation
- To prepare veld for crop production ✓
- To form a seedbed ✓
- To break hardened soils/plough layer/pan ✓
- To control weed ✓
- Improve aeration/drainage ✓ (Any 2) (2)
2.7 Precision farming
2.7.1 Debate principle of precision farming
- No✓, farmer does not adhere to principles of precision farming ✓
OR - No accurate fertilisation✓ or irrigation
- no chemical soil analysis ✓ (2)
2.7.2 Farming practices to increase precision farming
- Chemical soil analysis ✓
- Fertiliser application according to chemical soil status ✓
- Fertiliser spread throughout the season/as plant grow ✓
- Irrigation scheduling/schedule irrigation according to plant growth ✓
- Take amount of rainfall into account for irrigation ✓ (Any 4) (4)
[50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
3.1 Budget
3.1.1 The management principle that this budget addresses
- Financial planning ✓ (1)
3.1.2 THREE possible markets
- Livestock auctioning ✓
- Farm gate marketing ✓
- Manure retailers ✓ (3)
3.1.3 Calculate the possible profit or loss
- profit/loss = total income – total expenditure
= R477 500, 00 − R113 564,00 ✓
= R363 936,00 ✓ profit✓ (3)
3.1.4 TWO possible ways to increase income
- Find more markets ✓
- Add value to the product/processing ✓
- Sell at markets with higher prices ✓
- Find a different place/time to auction to get higher prices ✓ (Any 2) (2)
3.1.5 Identification of the section of a business plan
- Financial aspects/budget ✓
- Marketing ✓ (2)
3.2 Entrepreneurship
3.2.1 FOUR main distinct phases of the entrepreneurial process
- Identify and evaluate the opportunity/Notice a need ✓
- Develop the business plan ✓
- Determine the resources required ✓
- Start and manage the agribusiness ✓ (4)
3.2.2 Economic importance of a business plan
- Determine the possible income/profit ✓
- Compare different alternatives to choose the best one ✓
- Needed for financial institutions to obtain credit ✓
- Make the management and control on financial aspects easier ✓
- Determine viability of a new enterprise ✓ (5)
3.3 THREE important reasons of reviewing the business plan
- To provide for any changes in the market ✓
- To help the owner to make the best use of opportunities ✓
- To be prepared for possible events ✓
- Adopt the plan to any changes in the external environment ✓ (Any 3) (3)
3.4 Price setting
3.4.1 A factor that determines price
- Supply ✓
- Demand ✓ (Any 1) (1)
3.4.2 Line graph to represent 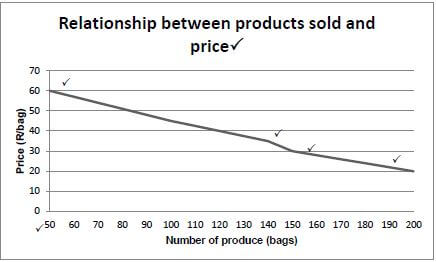
Rubric:
- Correct heading ✓
- Correct calibration or labelling of both axes ✓
- Graph start at (50; 60) ✓
- Straight line to (140; 35) ✓
- Short dip in line to (150; 30) ✓
- Straight line from (150: 30) to (200; 20) ✓ (6)
3.4.3 The values where greatest number of bags were bought
- At the price of R20,00 ✓: 200 bags ✓
OR - (200 bags ✓; R20,00 ✓) (2)
3.5 Marketing
3.5.1
- The marketing strategy
Product – consider- Quality of the product ✓
- Design of packaging the product ✓
- The size of the product ✓
- The variety of the products ✓
- The brand/commercial name ✓ (Any 3) (3)
- Placement - consider
- Process of distributing the product from one point to the other ✓
- Transportation, storage and refrigeration of the product ✓
- Logistics/the control of movement of goods ✓ (Any 2) (2)
3.5.2 THREE marketing costs
- Packaging costs ✓
- Handling costs ✓
- Transport costs ✓
- Product losses ✓
- Promoting costs ✓ (Any 3) (3)
3.6 Statements
3.6.1 List farm assets
- Fixed assets
- Borehole ✓
- Farm shed ✓
- Land ✓ (Any 2) (2)
- Current assets
- Pesticides ✓
- Fertilizers ✓
- Cash ✓ (Any 2) (2)
- Medium term assets
- Tractor ✓
- Farm vehicle ✓
- Livestock ✓ (Any 2) (2)
3.6.2 Statement of assets and liabilities
- Balance sheet ✓ (1)
3.7 THREE reasons for returning items
- Incorrect items received ✓
- Faulty items received ✓
- Business/farmers not satisfied with the purchased items ✓ (3)
[50]
QUESTION 4: HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
4.1 Storage
4.1.1 The advantages of storing farm products on the farm after harvesting
- Products can be sold when there are better prices on the market ✓
- Products can be stored and processed on the farm to add value and increase income ✓
- Storing is essential to buffer irregular supply ✓
- No external storage costs ✓
- To provide a regular flow of products to the consumer throughout the year ✓ (Any 2) (2)
4.1.2 Requirements for storage of agricultural products
- Dry ✓
- Well ventilated ✓
- Cool ✓
- Dark place ✓ (4)
4.2 Labelling Act 54 of 1972
- To protect consumers from buying contaminated food ✓
- To protect consumers from misleading labels ✓ (2) 4.3 Behaviour of micro-organisms at different temperatures
4.3.1 5–10 °C
- Microbes are inactive /not very active ✓ (1)
4.3.2 Above 100°C
- Microbes are killed ✓ (1)
4.3.3 Below 0°C
- Microbes are dormant ✓ (1)
4.4 Principles that should be part of a food handling strategy
- Management commitment to healthy/hygienic procedures ✓
- Education and training on preventative handling ✓
- Health interviews to ensure good hygienic procedures ✓
- Reporting illness of workers to management ✓
- Applying basic good/correct food handling practices ✓
- Applying basic personal hygiene practices ✓ (Any 4) (4)
4.5 Legal documents that regulate importing of meat and dairy products into South Africa
- Import permit ✓
- Veterinary health certificate ✓ (2)
4.6 Farmer as an agritourism entrepreneur
- To promote the farm as an agritourist destination by direct selling of products ✓
- By establishing educational facilities for schools and communities ✓ (2)
4.7 Preserving
4.7.1 Pasteurisation and sterilisation
Pasteurisation
- High temperatures (72°C–90°C)✓
- Longer period of time (15–40 minutes) ✓
Sterilisation
- Very high temperatures (90°C–105°C) ✓
- For very short time (30–40 seconds) ✓ (4)
4.7.2 TWO acids in preserving of food
- Benzoic acid ✓
- Propionic acid ✓
- Scorbutic acid ✓ (2)
4.8 The planning process
- Formulate aims and objectives ✓
- Collect ideas and information and organise it ✓
- Consider all variables which cannot be controlled ✓
- Consider various possible methods of action then decide on a particular production in farming ✓
- Draw up a plan of action for a particular production direction ✓
- Evaluate the plan to eliminate possible short comings ✓ (6)
4.9 Niche market
4.9.1 Niche market
- Specific market you give all your attention to ✓
- With special attention to a specific market segment ✓ (2)
4.9.2 Steps followed in establishing a niche market
- Identify the niche market ✓
- Write down the goals of the market ✓
- Decide which resources you need for the undertaking of the niche marketing ✓
- Determine the resources not available and how to compensate for them ✓
- Develop a business plan ✓ (5)
4.10 Management functions
- Planning and Decision making ✓
- Organising ✓
- Motivation and Leadership ✓
- Control ✓
- Coordination and evaluation ✓ (5)
4.11 Safety requirements for processing agricultural products
- Wear protective clothing at all times in the processing unit ✓
- Provide a first aid kit at different stations ✓
- Train first aid staff on a regularly basis ✓
- Train staff on safe handling of machinery ✓
- Train staff on safety rules applicable in the processing plant ✓
- Clean the place regularly during the day or in case of spoilage ✓
- Identify and indicate hazardous areas by proper methods ✓ (Any 4) (4)
4.12 Steps is the management control process
- Develop norms and standards for control ✓
- Measure real performance ✓
- Measure and evaluate deviation ✓ (3)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 150
GRAND TOTAL: 200