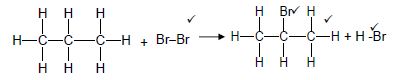TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupQUESTION 1
1.1 B ✓✓ (2)
1.2 D ✓✓ (2)
1.3 D ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C ✓✓ (2)
1.5 A ✓✓ (2)
[10]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing only carbon (atoms) and hydrogen (atoms). ✓✓ (2)
2.2.1
 | Marking criteria/Nasienkriteria:
|
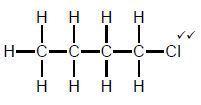
 | Marking criteria/Nasienkriteria:
|
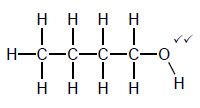
2.3 Methyl✓ ethanoate ✓(2)
2.4.1 Alkane ✓ (1)
2.4.2 Ester ✓ (1)
2.5.1 Structural isomers are organic molecules with the same molecular formula, ✓ but different structural (formulae). ✓ (2)
2.5.2 Functional (isomer) ✓ / (1)
[13]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 London/Dispersion/Induced Dipole (forces)✓
London/Dispersie-/Geïnduseerde dipool (kragte) (1)
3.1.2 A ✓ (1)
3.1.3
- A is a straight chain/unbranched/has larger surface area/less spherical/has a longer chain length than B ✓✓(2)
OR - B has a branch/has a smaller surface area /more spherical/has a shorter chain length than A
3.2.1
- A and C have the same chain length/number of carbon atoms/there is only one independent variable/they only differ in terms of fuctional group/homologous series ✓✓ (2)
3.2.2 C ✓ (1)
3.2.3
- A contains London/dispersion/induced dipole forces only, and C (in addition to London and dipole-dipole forces) contains hydrogen bonds. ✓
- Hydrogen bonds are stronger than London forces / Intermolecular forces of C are stronger than those of A/Intermolecular forces of A are weaker than those of C. ✓
OR - London/dispersion/Induced dipole forces are weaker than hydrogen bonds.
- More energy is needed to overcome stronger hydrogen bonds than weak London forces/More energy is needed to overcome stronger intermolecular forces in C than in A.✓
OR - Less energy is required to overcome weaker London forces than strong hydrogen bonds/Less energy is required to overcome weaker intermolecular forces in A than in C. (3)
3.3 B, A, C and/en D. ✓✓ (2 or/of 0) (2)
[12]
QUESTION 4
4.1.1 Addition/Hydrogenation ✓
4.1.2 Substitution ✓
4.2.1 Platinum/Pt ✓
OR
Palladium/Pd
OR
Nickel/Ni / (1)
4.2.2 (Mild) heat/Sunlight/UV light (Matige) hitte/Sonlig/UV lig ✓
No water/Geen water (1)
4.3.1
Marking criteria
|
(4)
4.3.2
- Carbon dioxide ✓
- Water ✓
OR - CO2
- H2O
(2)
4.4.1 Doping ✓ (1)
4.4.2 Intrinsic semiconductor is a pure semiconductor ✓✓ (2)
4.4.3
- An N-type semiconductor is a semiconductor with excess electrons/negative charge carriers, ✓✓/ it is formed when an intrinsic semiconductor is doped with pentavalent impurity
- A p-type semiconductor is a semiconductor with positive hole/charge carriers, ✓✓/ it is formed when an intrinsic semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity. (4)
[17]
QUESTION 5
5.1.1 Copper(II) ions ✓ (1)
5.1.2 Chloride ions ✓(1)
5.2.1 Positive (electrode) ✓ (1)
5.2.2 Negative (electrode) ✓ (1)
5.3 Oxidation is the loss of electrons ✓✓/ an increase in oxidation number
5.4 2Cℓ(aq) → Cℓ2 +2e- ✓✓ (2)
| Marking criteria Cℓ2(g) + 2e- ← 2Cℓ-(aq) (2/2 ) 2Cℓ-(aq) ⇌ Cℓ2(g) + 2e- (½) 2Cℓ-(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Cℓ2(g) ( 0/2 ) 2Cℓ-(aq) ← Cℓ2(g) + 2e- ( 0/2 ) NOTE: Do not penalise if the phases are not included or an electron charge is omitted. Penalise 1 mark if the charge on the chloride ion is omitted |
5.5 Reducing agent is a substance that is oxidised/loses electrons. ✓✓
Accept: Reducing agent is a substance that undergoes oxidation. (2)
5.6
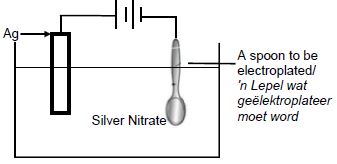 |
Marking criteria
(3) |
[13]
QUESTION 6
6.1.1 Galvanic /voltaic (cell)✓ (1)
6.1.2 Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)✓ → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) ✓
NOTE: Do not penalise if phases are omitted (2)
6.1.3
| OPTION | OPTION |
| Eθcell = Eθcathode - Eθanode ✓ = 0,34 ✓- (- 0,76) ✓ = 1,10 V ✓ | Zn → Zn 2+ + 2e- -(-0,76) ✓ Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (0,34)✓ Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu ✓ (1,10 V) ✓ |
ACCEPT any other relevant formula on the data sheet
Penalise 1 mark if unconventional abbreviation is used or there is omission in the formula.
(4)
6.2.1 Reaction/ (1)6.2.2
Magnesium is a stronger reducing agent than zinc ions ✓ therefore it will reduce zinc ions to zinc ✓
OR
Zinc ions are weaker reducing agent that magnesium, therefore magnesium will reduce zinc ions to zinc (metal).
OR
Nickel is a weaker reducing agent than zinc ions therefore it will NOT reduce zinc ions to zinc.
OR
Zn ions are stronger reducing agent than nickel, therefore nickel will not reduce zinc ions to zinc (metal).
OR
Magnesium is a stronger reducing agent than nickel, therefore magnesium will reduce zinc ions to zinc and nickel will not.
[10]
TOTAL 75