MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMATHEMATICS PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MEMORANDUM
MAY/JUNE 2021
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out an attempt of a question and not redone the question, mark the crossed out version.
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the marking memorandum. Stop marking at the second calculation error.
- Assuming answers/values in order to solve a problem is NOT acceptable.
GEOMETRY
- S - A mark for a correct statement
(A statement mark is independent of a reason) - R - A mark for the correct reason
(A reason mark may only be awarded if the statement is correct) - S/R - Award a mark if statement AND reason are both correct
QUESTION 1
1.1
| 26 | 13 | 3 | 18 | 12 | 34 | 24 | 58 | 16 | 10 | 15 | 69 | 20 | 17 | 40 |
1.1.1
- x = 375
15
x = 25 MB
Answer only: Full marks (2) - σ = 17,65 MB (1)
1.1.2
25 + 17,65 = 42,65
2 days ? (2)
1.1.3
Overall x = 80 x 25
100
= 20 MB
375 + x = 20
30
x = 600 - 375
= 225
maximum total amount of data that Sam must use for the remainder of the month: 225 MB
(3)
1.2
| Wind speed in km/h (x) | 2 | 6 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 17 | 11 | 24 | 13 | 22 |
| Temperature in °C (y) | 28 | 26 | 22 | 22 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 19 | 26 | 19 |
1.2.1
a = 29,35
b = -0,46
y = 29,35 - 0,46x
(3)
1.2.2
y = 25,20 °C (calculator) OR
y = 29,35 - 0,46(9)
y = 25,21 °C ?? answer
(2)
? substitution
? answer
(2)
1.2.3
b < 0 , indicating that as the wind speed increases the temperature decreases.
? interpretation (1)
[14]
QUESTION 2
| Number of days absent | Number of learners | Cumulative frequency |
| 0 ≤ x < 5 | 34 | 34 |
| 5 ≤ x < 10 | 45 | 79 |
| 10 ≤ x < 15 | 98 | 177 |
| 15 ≤ x < 20 | 43 | 220 |
| 20 ≤ x < 25 | 7 | 227 |
| 25 ≤ x < 30 | 3 | 230 |
2.1 Modal class: 10 ≤ x < 15
? answer (1)
2.2 177 learners
? answer (1)
2.3 230 learners
? answer (1)
2.4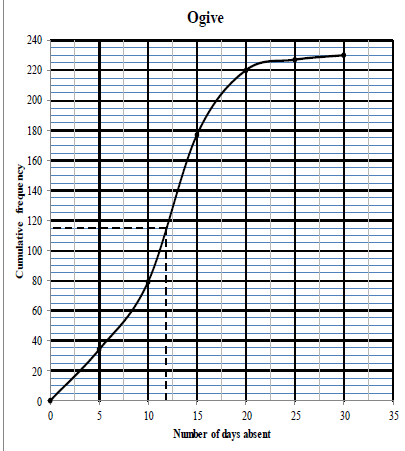
?grounding at (0; 0)
?shape
?upper limits
?All other points correct
2.5 The median is at position 115.
⸫value of median is 12 days (accept 11 – 14) Answer only: Full marks
? reading off at 115
? answer
(2)
[9]
QUESTION 3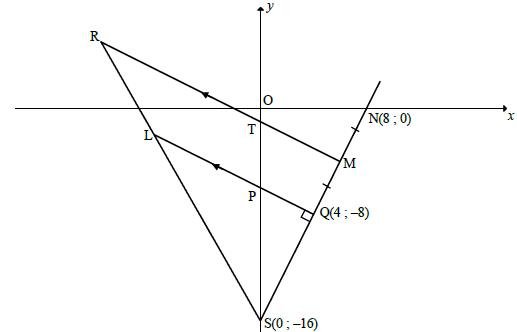
3.1
M(4 + 8 ; -8 + 0)
2 2
M(6; 4)
xM
yM
(2)
3.2
mNS =0 - (-16) or mNQ =0 - (-8) or mQS =-8 - (-16)
8-0 8-4 4-0
= 2
?subst N and Q or N and Q or Q and S into gradient formula
?answer
(2)
3.3
mLQ x 2 = -1 [LQ ⊥ NS]
mLQ = -½
-8 = -½(4) + c OR y + 8 = -½(x +4)
c = -6 y + 8 = -½x + 2
y = -½x - 6
?mLQ
? substitution of Q
? calculation of c or simplification
(3)
3.4 OS is the radius of circle passing through S
(x - 0)2 + (y - 0)2 = (16)2
x2 + y2 = 256
Answer only: Full mark
? identifying radius = 16
? Equation of circle
(2)
3.5
mRM = mLQ = -½ [RM || LQ]
- 4 = -½ (6) + c OR y + 4 = -½ (x - 6)
c = -1 y + 4 = -½ x + 3
y = -½x - 1
? mRM
? substitution of M(6; - 4)
? coordinates of T
(3)
3.6
T(0; -1) , P(0; -6) and S(0; -16)
PS = 10 units and TS = 15 units
LS = PS = 2 [prop theorem; RM || LP] OR [line || one side of Δ/lyn]
RS TS 3
Answer only: Full marks
? PS = 10 units
? TS = 15 units
? answer
(3)
OR
M(6 ; - 4), Q(4 ; - 8) and S(0 ; -16)
MS = √180 = 6√5 and QS = 80 = 4√5
LS = QS = 2 [prop theorem; RM || LQ] OR [line || one side of Δ/lyn]
RS MS 3
Answer only: Full marks
?MS = 6√5
QS = 4√5
? answer
(3)
3.7
area of PTMQ = area of ΔTSM – area of ΔPSQ
= ½ST. ⊥ hM -½.PS. ⊥ hQ
= ½(15)(6) - ½(10)(4)
= 45 – 20
= 25 square units
? area of ΔTSM – area of ΔPSQ
? area ΔTSM = 45
? area ΔPSQ = 20
? answer
(4)
OR
TM = √45 =3√5 = 6,71
MQ= √20 = 2√5 = 4,47
PQ =√20 = 2√5 = 4,47
area of trapezium PTMQ =½(3√5 + 2√5)(2√5)
= ½ (5√5)(2√5)
= 25 square units
? TM =3√5
MQ = 2√5
PQ = 2√5
? area of trapezium = ½
(sum of ||sides)(height)
? substitute into formula
? answer
(4)
OR
MQ √20 = 2√5
PQ √20 = 2√5
TP √5
area of PTMQ = area of ΔMTP + area of ΔPQM
area of PTMQ = ½TP x ⊥ hM + ½.MQ x PQ
area of PTMQ = ½(5) x 6 + ½(2√5 )(2√5 )
area of PTMQ = 10 + 15 = 25
? area of ΔMTP + area of ΔPQM
? area ΔMTP = 10
? area ΔPQM = 15
? answer
(4)
[19]
QUESTION 4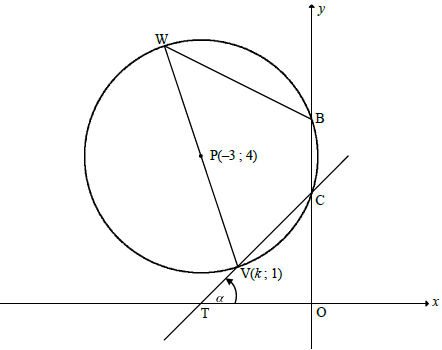
4.1
PV = r = √10
PV = √(k - (-3))2 + (1 - 4)2 = √10
(PV)2 = (k - (-3))2 + (1 - 4)2 = 10
k2 + 6k + 9 + 9 = 10 OR (k + 3)2 + 9 = 10
k2 + 6k + 8 = 0 (k + 3)2 = 1
(k + 4)(k + 2) = 0 k + 3 = 1 or k + 3 = -1
k = -4 or k = -2
k = -2
? PV = r = √10
? substitution into distance formula
? standard form
? factors
? answer
(5)
4.2
x2 + 6x + y2 - 8y +15 = 0
y-intercepts: (0)2 + 6(0) + y2 - 8y + 15 = 0
(y - 3)( y - 5) = 0
yC = 3 or yB = 5
BC = 2 units
? x = 0
? factors
? both values
? answer
(4)
4.3.1
mTC = 3 - 1
0- (-2)
= 1
tan a = 1
a = 45º
? substitution into gradient formula
? tan a = 1
? answer
(3)
OR
y = mx + 3
1 = m(-2) + 3
mTC = 1
tan a = 1
a = 45º
? substitution into equation of a line
? tan a = 1
? answer
(3)
4.3.2
BCV = 135º [ext ∠ of Δ]
VWB = 45º [opp ∠s of cyclic quad]
Answer only: Full marks
? BCV = 135º
? answer
(2)
OR
TCO = 45º [∠s of Δ]
VWB = 45º [ext ∠s of cyclic quad]
Answer only: Full marks
? TCO = 45º
? answer
(2)
4.4.1
Q(-3; - 2)
? xQ ? yQ (2)
4.4.2
(x + 3)2 + (y + 2)2 = 10
? LHS ? RHS (2)
4.4.3
x = -2 or x = -4 (2)
[20]
QUESTION 5
5.1 tan(-x).cos x.sin(x -180º) - 1
= -tan x.cos x.sin(-(180º - x)) -1
= -sin x .cos x.(- sin x) - 1
cos x
= sin2 x -1
= -cos2 x
? –tan x
? –sin x
cos x
? sin 2 x -1
? answer
(5)
5.2.1
cos 215°
= –cos 35°
= –m
? reduction
? answer
(2)
5.2.2 sin 20°
= cos 70°
= cos 2(35º)
= 2 cos2 35º - 1
= 2m2 - 1
? co-function
? double angle expansion
? answer in terms of m
(3)
OR
= sin (55° – 35°)
= sin55°cos35° – cos55°sin35°
= m.m -√1 - m2 . √1 - m2
= m2 - (1 - m2)
= 2m2 - 1
? compound angle expansion
? cos 55° √1 - m2 or
sin 35° √1 - m2
? answer in terms of m
(3)
5.3
cos 4x.cos x + sin 4x.sin x = -0,7
cos(4x - x) = -0,7
ref ∠ = 45,57…°
3x = 180° - 45,57...° + k.360° or 3x = 180° + 45,57...° k.360°
3x = 134,43° + k.360° or 3x = 225,57° + k.360°
x = 44,81° + k.120° ; k ∈ Z x = 75,19° + k.120° ; k ∈ Z
? compound angle
? 3x = 134,43° or 225,57°
? x = 44,81° or 75,19°
? + k.120°; k ∈ Z
(4)
5.4
RHS = cos2 x - sin2 x
LHS = sin 4x.cos 2x - 2cos 4x.sin x.cos x
tan 2x
= sin 4x.cos 2x - cos 4x.sin 2x
sin 2x
cos 2x
sin(4x - 2x)(cos 2x)
sin 2x
= cos 2x
=cos2 x - sin2 x
LHS = RHS
? sin 2x
? sin 2x
cos 2x
? sin(4x - 2x)
? cos 2x
(4)
[18]
QUESTION 6
6.1
1 - 2sin2 x = -sin x
2sin2 x -sin x -1 = 0
(2sin x +1)(sin x -1) = 0
sin x = -½ or sin x = 1
ref ∠ = 30° ref ∠ = 90°
x = 210º + k.360º x = 90º + k.360º
or x = 330º + k.360º
x = -150º or x = -30º or x = 90º
? identity
? factors
? sin x = -½
? sin x = 1
? –150° and –30°
? 90° (A)
(6)
OR
cos 2x = -sin x
cos 2x = -cos(90º - x)
2x = 180º - (90º - x) + k.360º or 2x = 180º + (90º - x) + k.360º
2x = 90º + x + k.360º or 2x = 270º - x + k.360º
x = 90º + k.360º x = 90º + k.12º
x = -150º or x = -30º or x= 90º
? co-functions
? 2x in quadrant 2
? 2x in quadrant 3
? both general solutions
? –150° and –30°
? 90° (A)
(6)
OR
cos 2x = -sin x
cos 2x = cos(90º + x)
2x = 90º + x + k.360º or 2x = 360º - (90º + x) + k.360º
x = 90º + k.360º or 3x = 270º + k.360º
x = 90º + k.120º
x = -150º or x =- 30º or x =90º
? co-functions
? 2x in quadrant 1
? 2x in quadrant 4
? both general solutions
? –150° and –30°
? 90° (A)
(6)
OR
cos 2x = -sin x
sin(90º - 2x) = -sin x
90º - 2x =180º x + k.360º or 90º - 2x = 360º - x + k.360º
x = -30º + k.120º x = -270º + k.360º
x = -150º or x = -30º or x=90º
? co-functions
? 90°–2x in quadrant 3
? 90°–2x in quadrant 4
? both general solutions
? –150° and –30°
? 90° (A)
(6)
6.2.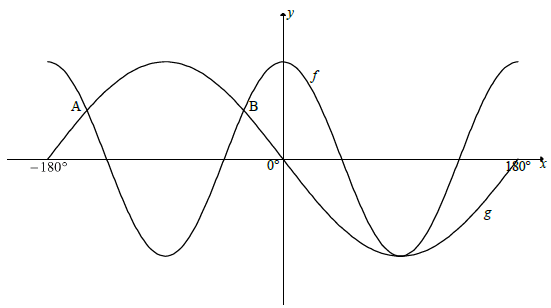
6.2.1
A(–150°; 0,5) B(–30°; 0,5)
AB = –30° – (–150°)
AB = 120° Answer only: Full marks
? AB = –30° – (–150°)
? answer
(2)
6.2.2
x ∈ (0º; 90º) or x ∈ (90º; 180º)
OR
0º < x < 90º or 90º < x < 180º
? x ∈ (0º; 90º)
? x ∈(90º; 180º)
(2)
6.2.3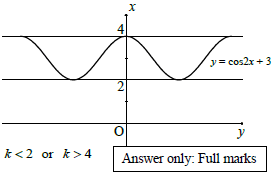
cos 2x = k - 3
k - 3 < -1 or k - 3 > 1
k < 2 or k > 4 Answer only: Full marks
OR
? graph of y = cos2x + 3
? k < 2 ? k > 4
(3)
[13]
QUESTION 7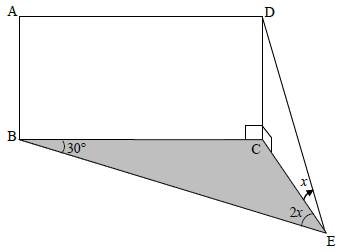
7.1
In ∆BCE:
CE = BC
sinB sinBEC
CE = BC
sin30º sin2x
CE = BCsin30º
sin 2x
? correct use of sine rule
? CE = BCsin30º
sin 2x
In ∆CDE:
DC = tan DEC
CE
DC = BC.sin30º (tan x)
sin 2x
DC = BC ( sin x )
4 sin x cos x cos x
DC = BC
4cos2x
? correct trig ratio
? Subst CE
? 2sin x cos x
? sin x
cos x
(6)
7.2
DC = BC
4cos2 30º
= BC
4(√3/2)2
= BC
3
BC = 3DC
But AB = DC [opp sides of rectangle]
BC = 3AB
Area of rectangle = (AB)(BC)
= (AB)(3AB)
=3AB2
? DC = BC
3
? BC = 3AB
? substitution into area formula
(3)
[9]
QUESTION 8
8.1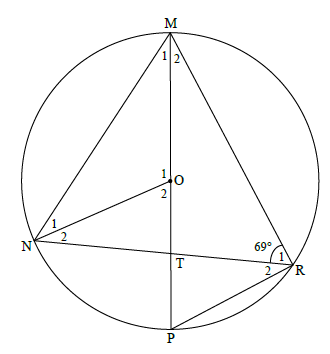
8.1.1
MRP = 90º [∠ in semi circl]
R2 =21º
(2)
8.1.2
O1 = 138º [∠ at centre = 2 × ∠ at circumference/midpts.
(2)
8.1.3
M1 = 21º [∠s in the same segment]
OR
M1 + N1 = 180º - 138º [sum of ∠s in ∆ ]
M1 = 21º [∠s opp equal sides]
(2)
8.1.4
O2 = 42º [∠s on a str line]
P = 42º [alt ∠s; NO || PR]
M2 = 48º [sum of ∠s in ∆]
OR
N2 = R2 = 21º [alt ∠s; NO || PR]
N1 = M1 = 21º [ ∠s opposite equal sides]
M2 = 48º [sum of ∠s of Δ NMR//]
(4)
8.2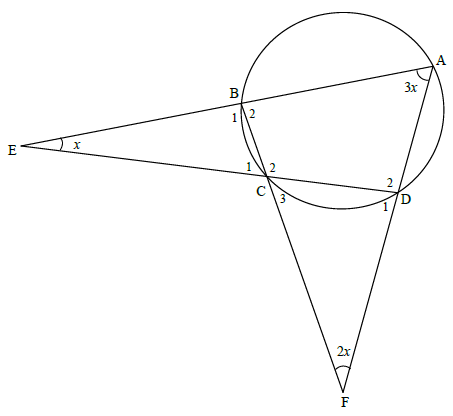
8.2
D1 = 4x [ext ∠ of ∆ ]
D2 = 180º - 4x [∠s on a str line]
B1 = 5x [ext ∠of ∆]
B1 = D2 [ext ∠ of cyclic quad/buite v kvh]
180º - 4x = 5x
9x = 180º
x = 20º
OR
C1 = 3x [ext ∠ of cyclic quad]
B2 = 4x [ext ∠ of ∆]
C1 = C3 = 3x [vert opp ∠s]
D2 = 5x [ext ∠ of ∆]
4x + 5x = 180º [opp∠ of cyclic quad]
x = 20º
(6)
OR
C3 = 3x [ext ∠of cyclic quad]
D1 = 4x [ext ∠ of ∆]
2x + 3x + 4x = 180º [sum of ∠s in ∆]
9x = 180º
x = 20º
(6)
[16]
QUESTION 9
9.1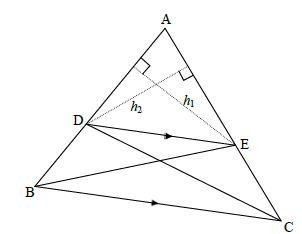
9.1 Constr: Join BE and CD and draw h1 from E ⊥ AD and h2 from D ⊥ AE
Proof:
area ∆ADE = ½AD x h1 =AD
area ∆BDE ½BD x h1 BD
area ∆ADE = ½AE x h2 = AE
area ∆DEC ½EC x h2 EC
area ∆ADE = area∆ADE [common]
But area ∆BDE = area ∆DEC [same base & height ; DE || BC]
area ∆ADE = area ∆ADE
area ∆BDE area ∆DEC
AD = AE
BD EC
? constr
? S ?R
(6)
9.2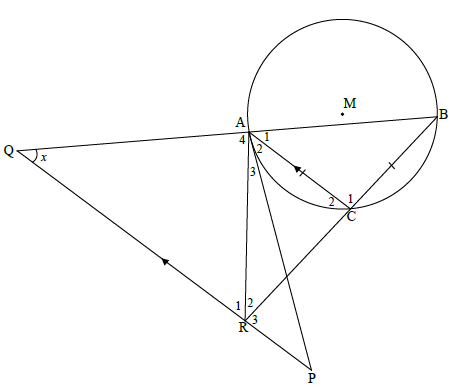
9.2.1
A1 = x [corresp ∠s; PQ || CA]
B = x [∠s opp equal sides]
A2 = x [tan-chord theorem]
P = x [alt ∠s; PQ || CA || CA]
(6)
9.2.2
B = P [proved in 9.2.1]
A, B, P and R are concyclic
ABPR is a cyclic quadrilateral [conv ∠s in the same segment]
(2)
9.2.3
BA = BC [prop th; AC || QP]
BQ BR
OR
[line || one side /lyn]
But QR = BR [sides opp = ∠s]
BA = BC
BQ QR
(3)
OR
In ΔABC and ΔBQR:
A1 = B = x [proved in 9.2.1]
B = Q = x [proved in 9.2.1]
C1 = BRQ = 180º - 2x [sum of ∠s of Δ ]
ΔABC ||| ΔBQR
BA = BC
BQ QR
OR
In ΔABC and ΔBQR:
A1 = B = x [proved in 9.2.1]
B = Q = x [proved in 9.2.1]
C1 = BRQ = 180º - 2x [sum of ∠s of Δ ]
Δ ABC ||| Δ BQR [∠∠∠]
BA = BC
BQ QR
OR
In Δ ABC and Δ QBR:
B is common
A1 = Q = x [corres ∠s; PQ || CA]
C1 = BRQ = 180º - 2x [sum of ∠s of Δ ]
Δ ABC ||| Δ QBR [ ∠∠∠ ]
But QR = BR [sides opp = ∠s]
BA = BC
BQ QR
(3)
[17]
QUESTION 10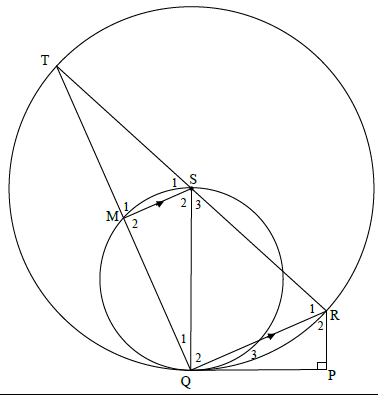
10.1.1
Q1 + Q2 = 90º [∠ in semi circle]
M2 = 90º [co-interior ∠, MS || QR]
SQ is a diameter [converse: ∠ in semi circle]
OR
MS || QR
TS = TM = 1 [prop theorem; SM || QR] OR
SR MQ 1 [line || one side of Δ]
TM = MQ
M2 = 90º [Line from centre bisects chord]
SQ is a diameter [converse:∠ in semi circle]
OR
SQ ⊥ QP [tan ⊥ rad]
SQ is a diameter [converse: tan ⊥ rad/]
(3)
10.1.2
In ΔRTQ and ΔRQP
T = Q3
Q1 + Q2 = 90º
Q1 + Q2 = P = 90º
R1 = R2
ΔRTQ ||| ΔRQP
RT = RQ
RQ RP
RT = RQ2
RP
? S ? R
? S
? S
? R
? ratio
(6)
OR
In ΔRTQ and ΔRQP
T = Q3 [tan-chord theorem]
Q1 + Q2 = 90º [co-interior ∠s, MS || QR] or [∠ in semi circle]
Q1 + Q2 = P= 90º
ΔRTQ ||| ΔRQP [∠∠∠]
RT = RQ
RQ RP
RT = RQ2
RP
? S ? R
? S
? S
? R
? ratio
(6)
10.2
QR = 28 units [midpoint theorem]
RP2 = 282 - (√640)2 [Pythagoras]
RP = 12 units
RT= RQ2
RP
RT = 282
12
RT = 196
3
Radius =98/3 3 units
? S
? RP = 12
[15]
TOTAL: 150