PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your examination number and centre number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of 11 questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, e.g. between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 D.
1.1 Inertia is the tendency of an object to …
- maintain its mass.
- continue in a state of non-uniform motion.
- remain at rest or in the state of uniform motion.
- maintain its velocity when a non-zero net force is acting on it. (2)
1.2 A person stands on a bathroom scale that is fixed to the floor of a lift, as shown in the diagram below.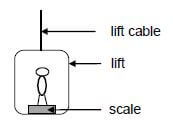
The reading on the scale is largest when the lift moves …
- upwards at a constant speed.
- downwards at a constant speed.
- upwards at a increasing speed.
- downwards at a increasing speed. (2)
1.3 An object is projected vertically upwards. Ignore air resistance.
As the object rises, its velocity …
- and acceleration are both directed upwards.
- and acceleration are both directed downwards.
- is directed upwards, but its acceleration is directed downwards.
- is directed downwards, but its acceleration is directed upwards. (2)
1.4 Ball P and ball Q, of the same mass, are dropped onto a concrete floor. Both balls hit the concrete floor at the same speed, v. Ball P rebounds with the same vertical speed, v, but ball Q rebounds with speed ½v.
Refer to the diagram below. Ignore air resistance.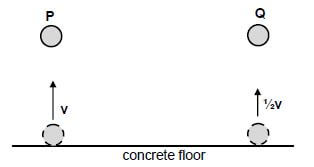
Which ONE of the following statements regarding the collision of EACH ball with the concrete floor is CORRECT?
- Kinetic energy is conserved for both balls P and Q.
- The change in momentum of ball P is greater than that of ball Q.
- The contact time with the floor is the same for both balls P and Q.
- Momentum is conserved for the collision of ball P, but not for that of ball Q. (2)
1.5 If the net work done on a moving object is POSITIVE, then we can conclude that the kinetic energy of the object …
- is zero.
- has increased.
- has decreased.
- has not changed. (2)
1.6 The spectrum produced by a moving asteroid, as observed from Earth, indicates that the light has shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum.
Which ONE of the following frequency combinations of the observed light and the distance between the asteroid and Earth is CORRECT? (2)
| FREQUENCY OF OBSERVED LIGHT | DISTANCE BETWEEN ASTEROID AND EARTH | |
| A | Increased | Decreases |
| B | Increased | Increases |
| C | Decreased | Decreases |
| D | Decreased | Increases |
1.7 Three charged spheres X, Y and Z, supported by insulating threads of equal length, hang from a beam, as shown in the diagram below.
Sphere X is negatively charged.
Sphere X attracts sphere Y, but repels sphere Z.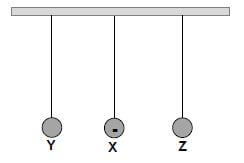
Which ONE of the following conclusions is CORRECT?
- Sphere Y is positively charged and sphere Z is negatively charged.
- Sphere Y is positively charged and sphere Z is positively charged.
- Sphere Y is negatively charged and sphere Z is negatively charged.
- Sphere Y is negatively charged and sphere Z is positively charged. (2)
1.8 In the circuit diagrams below, the cells and resistors are identical. The cells have negligible internal resistances.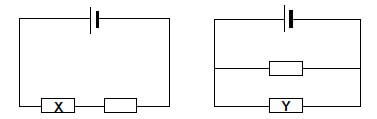
The power dissipated in resistor X is P. The power dissipated in resistor Y is …
- ¼P.
- ½P.
- 2P.
- 4P. (2)
1.9 Which ONE of the following actions will NOT cause an increase in the induced emf in a coil if the coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field?
- Rotating the coil faster
- Increasing the strength of the magnetic field
- Increasing the number of turns of the coil
- Replacing the coil with a coil of lower resistance (2)
1.10 A learner writes the following statements about the emission spectrum of light in a notebook:
- An emission spectrum is formed when certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation pass through a cold gas.
- The lines in the emission spectrum of an atom have the same frequency as the corresponding lines in the atom's absorption spectrum.
- An emission spectrum is formed when the atom makes transitions from a high-energy state to a lower energy state.
Which ONE of the following combinations of the statements above is CORRECT?
- (i) only
- (ii) only
- (ii) and (iii) only
- (i) and (iii) only (2) [20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
A block, of mass 8 kg, is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The 8 kg block, which is connected to a 2 kg block by means of a light inextensible string passing over a light frictionless pulley, starts sliding from point A, as shown below.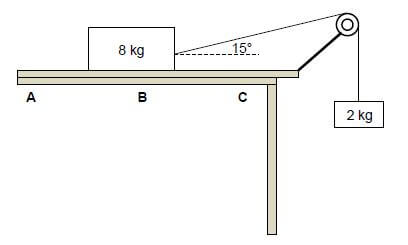
2.1 State Newton's Second Law in words. (2)
2.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram for the 8 kg block. (4)
2.3 When the 8 kg block reaches point B, the angle between the string and the horizontal is 15° and the acceleration of the system is 1,32 m·s-2.
2.3.1 Give a reason why the system is NOT in equilibrium. (1)
2.3.2 Use the 2 kg mass to calculate the tension in the string. (3)
2.3.3 Calculate the kinetic frictional force between the 8 kg block and the horizontal surface. (4)
2.4 As the 8 kg block moves from B to C, the kinetic frictional force between the 8 kg block and the horizontal surface is not constant. Give a reason for this statement. (1)
The horizontal surface on which the 8 kg block is moving, is replaced by another horizontal surface made from a different material.
2.5 Will the kinetic frictional force, calculated in QUESTION 2.3.3 above, change?Choose from: YES or NO. Give a reason for the answer. (2) [17]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
In a competition, participants must attempt to throw a ball vertically upwards past point T, marked on a tall vertical pole. Point T is 3,7 m above the ground. Point T may, or may not, be the highest point during the motion of the ball.
One participant throws the ball vertically upwards at a velocity of 7,5 ms-1 from a point that is 1,6 m above the ground, as shown in the diagram below. Ignore the effects of air resistance.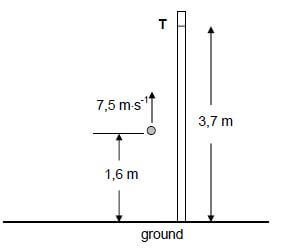
3.1 In which direction is the net force acting on the ball while it moves towards point T? Choose from: UPWARDS or DOWNWARDS. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.2 Calculate the time taken by the ball to reach its highest point. (3)
3.3 Determine, by means of a calculation, whether the ball will pass point T or not. (6)
3.4 Draw a velocity-time graph for the motion of the ball from the instant it is thrown upwards until it reaches its highest point.
Indicate the following on the graph:
- The initial velocity and final velocity
- Time taken to reach the highest point (2) [13]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
Initially a girl on roller skates is at rest on a smooth horizontal pavement. The girl throws a parcel, of mass 8 kg, horizontally to the right at a speed of 4 m.s-1. Immediately after the parcel has been thrown, the girl-roller-skate combination moves at a speed of 0,6 m.s-1. Ignore the effects of friction and rotation.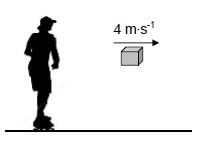
4.1 Define the term momentum in words. (2)
4.2 Will the girl-roller-skate combination move TO THE RIGHT or TO THE LEFT after the parcel is thrown? NAME the law in physics that can be used to explain your choice of direction. (2)
The total mass of the roller skates is 2 kg.
4.3 Calculate the mass of the girl. (5)
4.4 Calculate the magnitude of the impulse that the girl-roller-skate combination is experiencing while the parcel is being thrown. (3)
4.5 Without any further calculation, write down the change in momentum experienced by the parcel while it is being thrown. (2) [14]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below, not drawn to scale, shows a vehicle with a mass of 1 500 kg starting from rest at point A at the bottom of a rough incline. Point B is 200 m vertically above the horizontal.
The total work done by force F that moves the vehicle from point A to point B in 90 s is 4,80 x 106 J.
5.1 Define the term non-conservative force. (2)
5.2 Is force F a conservative force? Choose from: YES or NO. (1)
5.3 Calculate the average power generated by force F. (3)
The speed of the vehicle when it reaches point B is 25 m∙s-1.
5.4 State the work-energy theorem in words. (2)
5.5 Use energy principles to calculate the total work done on the vehicle by the frictional forces. (5) [13]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
The alarm of a vehicle parked next to a straight horizontal road goes off, emitting sound with a wavelength of 0,34 m. A patrol car is moving at a constant speed on the same road. The driver of the patrol car hears a sound with a frequency of 50 Hz lower than the sound emitted by the alarm. Take the speed of sound in air as 340 m∙s-1.
6.1 State the Doppler effect in words. (2)
6.2 Is the patrol car driving TOWARDS or AWAY FROM the parked vehicle? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
6.3 Calculate the frequency of the sound emitted by the alarm. (3)
6.4 The patrol car moves a distance of x metres in 10 seconds. Calculate the distance x. (6) [13]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
Three small identical metal spheres, P, S and T, on insulated stands, are initially neutral. They are then charged to carry charges of -15 x 10-9 C, Q and +2 x 10-9 C respectively, as shown below.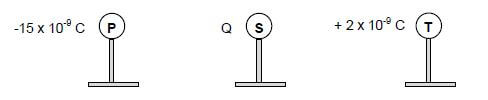
The charged spheres are brought together so that all three spheres touch each other at the same time, and are then separated. The charge on each sphere, after separation, is -3 x 10-9 C.
7.1 Determine the value of charge Q. (2)
7.2 Draw the electric field pattern associated with the charged spheres, S and T, after they are separated and returned to their original positions. (3)
The spheres, each with the new charge of -3 x 10-9 C, are now placed at points on the x-axis and the y-axis, as shown in the diagram below, with sphere P at the origin.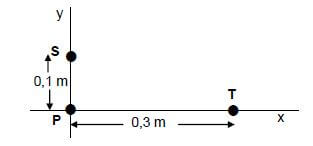
7.3 State Coulomb's law in words. (2)
Calculate the magnitude of the:
7.4 Net electrostatic force acting on sphere P (5)
7.5 Net electric field at the origin due to charges S and T (3)
7.6 ONE of the charged spheres, P and T, experienced a very small increase in mass after it was charged initially.
7.6.1 Which sphere, P or T, experienced this very small increase in mass? (1)
7.6.2 Calculate the increase in mass by the sphere in QUESTION 7.6.1. (3) [19]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
The battery in the circuit diagram below has an emf of 12 V and an internal resistance of 0,5 Ω. Resistor R has an unknown resistance.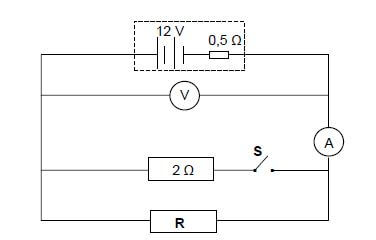
8.1 What is the meaning of the following statement? The emf of the battery is 12 V. (2)
The reading on the ammeter is 2 A when switch S is OPEN.
8.2 Calculate the:
8.2.1 Reading on the voltmeter (3)
8.2.2 Resistance of resistor R (2)
Switch S is now CLOSED.
8.3 How does this change affect the reading on the voltmeter? Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. Explain the answer. (4) [11]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
Learners perform an experiment to determine the emf (ε) and the internal resistance (r) of a battery using the circuit below.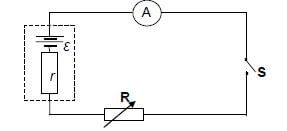
The learners use their recorded readings of current and resistance, together with the equation R = ε - r, to obtain the graph below.
I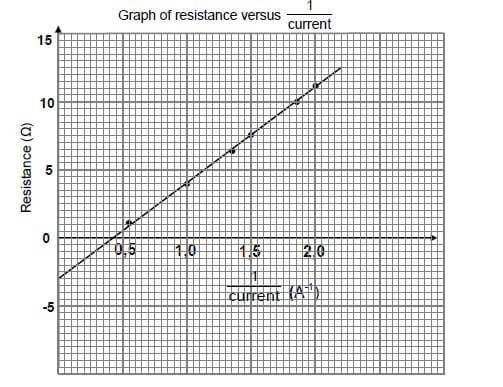
9.1 Which variable has to be kept constant in the experiment? (1)
9.2 Refer to the graph.
9.2.1 Write down the value of the internal resistance of the cell. (2)
9.2.2 Calculate the emf of the battery. (3) [6]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
10.1 In the simplified AC generator below, the coil is rotated clockwise.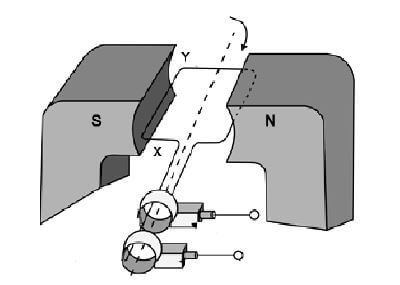
10.1.1 In which direction does the induced current flow in the coil? Choose from: X to Y or Y to X. (1)
10.1.2 On which principle or law is the working of the generator based? (1)
10.1.3 State the energy conversion that takes place while the generator is in operation. (2)
10.2 The voltage output for an AC generator is shown below.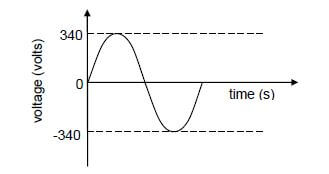
10.2.1Write down the maximum (peak) output voltage of the generator. (1)
A stove is connected to the generator above, and delivers an average power of 1 600 W.
10.2.2 Calculate the rms voltage delivered to the stove. (3)
10.2.3 Calculate the resistance of the stove. (3) [11]
QUESTION 11 (Start on a new page.)
The threshold frequencies of caesium and potassium metals are given in the table below.
METAL | THRESHOLD FREQUENCY |
Caesium | 5,07 x 1014 Hz |
Potassium | 5,55 x 1014 Hz |
11.1Define the term work function in words. (2)
11.2 Which ONE of the two metals in the table has the higher work function? Give a reason for the answer by referring to the information in the table. (2)
The simplified diagrams below show two circuits, A and B, containing photocells. The photocell in circuit A contains a caesium metal plate, while the photocell in circuit B contains a potassium metal plate.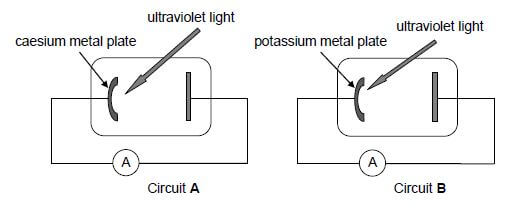
Ultraviolet light with the same intensity and wavelength of 5,5 x 10-7 m is incident on the metal plate in EACH of the photocells and the ammeter in circuit A registers a current.
11.3 By means of a calculation, determine whether the ammeter in circuit B will also register a current. (3)
11.4 Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron in circuit A. (5)
11.5 How will the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electron, calculated in QUESTION 11.4, change when the intensity of the incident light increases? Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. (1) [13]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m·s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 x 10-11 N·m2·kg-2 |
Radius of Earth | RE | 6,38 x 106 m |
Mass of Earth | ME | 5,98 x 1024 kg |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m·s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J·s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 x 109 N·m2·C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 x 10-31 kg |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE