ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
SEPTEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
- SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
- SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the number of the question above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully and start each question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 A perfectly competitive business makes a loss in the short run if …
- P = AC.
- P > AC.
- P < AC.
- P > AVC.
1.1.2 The demand curve of an oligopoly is …
- horizontal.
- vertical.
- kinked.
- upward sloping.
1.1.3 Consumers do not make rational decisions due to a(an) ...
- lack of information.
- improvement in technology.
- increase in income.
- decrease in interest rate.
1.1.4 Stagflation indicates the simultaneous existence of high inflation rates and ...
- high growth.
- low unemployment.
- high unemployment.
- low growth and high unemployment.
1.1.5 South African indigenous uniqueness is represented by …
- the Vredefort Dome.
- the Isimangaliso Wetland Park.
- Robben Island.
- Mapungubwe.
1.1.6 Resources that may become depleted if they are not well managed are known as … resources.
- renewable
- non-renewable
- natural
- infinite
1.1.7 If the rand depreciates, prices and inflation will …
- decrease.
- remain unchanged.
- increase.
- shrink.
1.1.8 In a monopoly, the demand curve is equal to the…
- marginal revenue.
- average revenue.
- average cost.
- marginal cost. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A.
Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Marketable permits 1.2.2 Pareto efficiency 1.2.3 Table Mountain 1.2.4 Variable costs 1.2.5 Agenda 21 1.2.6 Sunk costs 1.2.7 Command and control 1.2.8 Competition Commission |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Cost increases as production increases
1.3.2 Activities of tourists who visit museums and art galleries
1.3.3 A continuous fall in the general price level
1.3.4 Keeping resources intact for future generations
1.3.5 Costs and benefits to third parties which are not included in the market price
1.3.6 A market structure in which businesses have many competitors but each one sells a slightly different product (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO methods of non-price competition in monopolistic competition. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why do businesses in an oligopolistic market collude with one another? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graphs below and answer the questions that follow.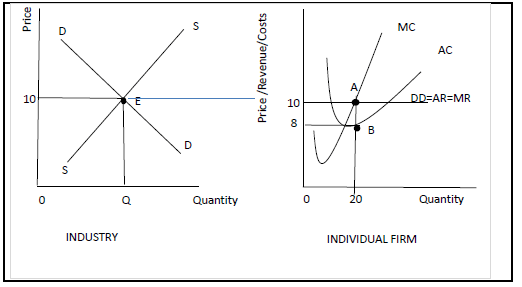
2.2.1 Identify the equilibrium point of the individual firm above. (1)
2.2.2 Which time period is depicted in the graph above? (1)
2.2.3 What is the reason for the downward sloping demand curve of the industry? (2)
2.2.4 Why are businesses in this industry referred to as price-takers? (2)
2.2.5 How will new entrants (businesses) affect the perfect market? (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
ICASA SET TO BREAK MULTICHOICE MONOPOLY
The Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) raised an inquiry into pay TV broadcasting and proposed to restrict, among others, Multichoice monopoly of premium sports content.
In redressing the recurring competition issues, major interventions were proposed such as shortening exclusive contracts, unbundling and splitting rights.
The CEO of Naspers, an affiliate of Multichoice, considered it ridiculous to do away with exclusive rights on sports broadcasting, claiming that they pay for every player and all the lights at the stadium and the backrooms.
2.3.1 Give ONE form of barrier to entry in a monopoly. (1)
2.3.2 What is the nature of the products sold by monopolies? (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term natural monopoly. (2)
2.3.4 Why would it be necessary to break Multichoice’s monopoly? (2)
2.3.5 How would demerit goods contribute to market failure? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 With the aid of a fully labelled graph, explain the supply curve of a business in a perfect market. (8)
2.5 Evaluate the effects of monopolies on an economy. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 List any TWO goods where prices are administered by the government. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why do countries engage in deforestation? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
CONSUMER PRICE INDEX
A consumer price index (CPI) measures changes in the price level of a market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.
The CPI is a statistical estimate constructed by using the prices of a sample of representative items whose prices are collected periodically. Basic types of data needed to construct the CPI are price data and weighting data.
The annual percentage change in CPI is used a measure of inflation.
3.2.1 List any example of a good or service on which CPI’s are based. (1)
3.2.2 How is the Consumer Price Index (CPI) calculated? (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term hyperinflation. (2)
3.2.4 Briefly explain consumer spending as a cause of demand pull inflation. (2)
3.2.5 Why are products with volatile prices excluded from the consumer price index? (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS CUTS BY 2050
Several states and countries adopted targets for steep reductions in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, but little physically realistic modelling of the energy and economic transformations has been done.
Cuts to greenhouse gas emissions will spare the planet half the trauma expected over the next century as the Earth warms.
3.3.1 Give any country that is part of G-8 nations. (1)
3.3.2 According to the extract, what are G-8 nations known for? (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term environmental sustainability. (2)
3.3.4 Explain the impact of greenhouse gases on the environment. (2)
3.3.5 How can the economy be developed without harming the environment? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Explain fiscal and monetary policies as measures to combat inflation. (2 x 4) (8)
3.5 How successful has the South African government been in support of a green economy? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO features of public goods. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 What positive effect will the granting of property rights have on the environment? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
THE INCREASE IN VAT WILL DRIVE INFLATION HIGHER
Middle-class consumers will bear the brunt of tax reforms announced in South Africa’s 2018/19 budget, despite there being no increases to personal income taxes, say experts.
The researcher suggested that following the first VAT increase in SA’s democratic history, consumers would pay more for all goods except the most basic food items, suggesting the middle class would be hardest hit.
4.2.1 Give an example of a basic food item that is exempted from VAT. (1)
4.2.2 Which type of inflation is depicted in the extract above? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe inflation targeting in South Africa. (2)
4.2.4 How are creditors affected by inflation? (2)
4.2.5 How can the effect of an increase in VAT be combated? (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
CELL C WILL KEEP THE ‘GIANTS’ ON THEIR TOES
The mobile telecom sector is one of the industries that is dominated by two large players, Vodacom and MTN.
Cell C’s entry in the telecom sector, and that of other cellular phone network operators challenged what was effectively a duopoly that had sewn up the market.
The recapitalisation of Cell C will ensure that the telecoms giants are kept on their toes for the foreseeable future.
4.3.1 Give ONE type of non-price competition that exists in oligopolies. (1)
4.3.2 What characterises the products sold by oligopolies? (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term duopoly. (2)
4.3.4 What makes it difficult for new businesses to enter into an oligopoly? (2)
4.3.5 How is the economy negatively affected by oligopolistic tendencies? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain biodiversity loss and chemical waste as problems in sustaining the environment. (2 x 4) (8)
4.5 What does the South African government hope to achieve through competition policies? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
Your answer will be assessed as follows.
| STRUCTURE OF ESSAY MARK | ALLOCATION |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body Additional part: Give own opinion/Critically discuss/Evaluate/Critically |
Max. 26
Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
| TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- With the aid of graphs, discuss in detail state intervention as a consequence of market failures under the following headings:
- Minimum wages (13 marks)
- Subsidies on goods and services (13 marks) (26 marks)
- How can cost benefit analysis reduce market failure? (10 marks) [40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss in detail the effects of tourism. (26 marks)
- How can government sustain the positive impact of tourism? (10 marks) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150