TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
SEPTEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full NAME and SURNAME in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of NINE questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWERBOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number your answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two sub-questions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for eg. 1.11 E.
1.1 Study the structural formula of an organic compound below.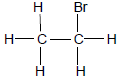
The homologous series to which the compound belongs is …
- alkanes.
- ketones.
- aldehydes.
- haloalkanes. (2)
1.2 Consider the reaction:
CH3Br + KOH CH3OH + KBr
The type of reaction taking place is …
- addition.
- hydration.
- substitution.
- combustion. (2)
1.3 Study the vapour pressure versus temperature graphs for a secondary and a tertiary alcohol. Both compounds have the molecular formula C4H10O. The atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa.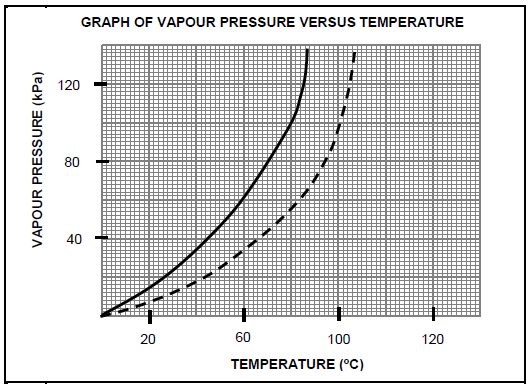
Which ONE of the following is the boiling point of the TERTIARY alcohol?
- 80ºC
- 70ºC
- 100ºC
- 110ºC(2)
1.4 In a redox reaction a reducing agent always:
- Loses electrons
- Gains electrons
- Undergoes reduction
- Undergoes a decrease in oxidation number (2)
1.5 A Technical science learner wants to store copper (II) sulphate solution CuS04in a metal container. The container must not develop a leak due to a chemical reaction between the metal and the solution.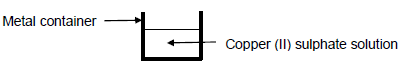
Which ONE of the following metals must the learner use as the container?
- Aℓ
- Ni
- Ag
- Sn (2)
1.6 Which ONE of the following CORRECTLY describes the energy change in an electrolytic cell?
- Electrical energy changes to chemical energy.
- Electrical energy changes to mechanical energy.
- Chemical energy changes to electrical energy.
- Chemical energy to mechanical energy. (2)
1.7 The image of a candle is found to be 5 cm behind a flat mirror.
The distance between the candle and the mirror is …
- 0 cm.
- 5 cm.
- longer than 5 cm.
- shorter than 5 cm. (2)
1.8 The bending of light as it moves from one medium to another called:
- Dispersion
- Diffraction
- Refraction
- Reflection (2)
- Copper (II) sulphate solution
1.9 Consider the section of the electromagnetic spectrum below.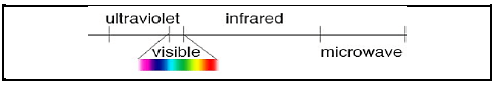
Which ONE of the electromagnetic radiations shown in the diagram above has the longest wavelength?
- Infrared
- Ultraviolet
- Microwave
- Visible light (2)
1.10 A ray of light passes from glass to air as shown in the diagram below.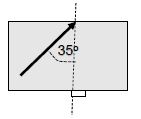
The critical angle for glass is 38o.
The light ray will undergo the following:
- Reflection
- Total internal reflection
- Refraction towards the normal
- Refraction away from the normal (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a NEW page.)
The letters A to F represent six organic compounds.
| A | B | Polythene | |
| C | 2-chloro-2-methylpropane | D | O ΙΙ CH3CH2 — O — C — CH2CH3 |
| E | H O H Ι ΙΙ Ι H — C — C — C —H Ι Ι H H | F | 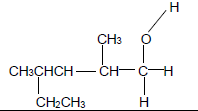 |
2.1 Write down the LETTER that represents the following:
2.1.1 A hydrocarbon (1)
2.1.2 A ketone (1)
2.1.3 A compound with the general formula CnH2n-2 (1)
2.2 Write down the NAME of the homologous series to which EACH of the following belong:
2.2.1 Compound A (1)
2.2.2 Compound D (1)
2.2.3 Compound F (1)
2.3 Write down the structural formula of compound C. (2)
2.4 Write down the IUPAC name of each of the following:
2.4.1 Compound E (2)
2.4.2 Compound F (3)
2.5 Write down the condensed structural formula of a positional isomer of compound A. (2)
2.6 Compound D is prepared from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Write down the:
2.6.1 Structural formula of the carboxylic acid used (2)
2.6.2 IUPAC name of compound D (2)
2.7 Compound B is a macromolecule from which synthetic materials derived from organic compounds are produced.
2.7.1 Define the term macromolecule. (2)
2.7.2 Write down single term for the underlined phrase (1)
2.7.3 Write down the structural formula of polythene. (2)
[24]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a NEW page)
During an investigation to compare the viscosity of alkanes, learners used a stopwatch to measure the time it takes a FIXED volume of each alkane to flow from a pipette as shown below.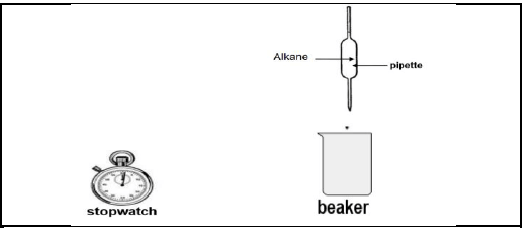
The learners’ results are recorded in the table below.
| COMPOUND | ALKANE | TIME OF FLOW (minutes) |
| A | 2,2 – dimethylpropane | 0,214 |
| B | 2 – methylbutane | 0,297 |
| C | pentane | 0,350 |
3.1 Define the term viscosity. (2)
3.2 Which alkane (A, B or C) has the HIGHEST viscosity? (1)
3.3 Explain fully the answer to QUESTION 3.2. (3)
3.4 Which alkane (A, B or C) has the HIGHEST vapour pressure? (1)
3.5 Compounds A and B have LOWER boiling points than compound C.
Write down a definition of boiling point. (2)
3.6 Compound C is a component of petrol.
Write down a balanced equation for the reaction of compound C with excess oxygen. (3)
[12]
QUESTION 4
The flow diagram given below shows how prop-1-ene can be converted to other organic compounds.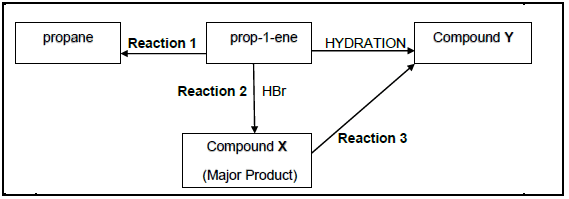
4.1 Is propane a SATURATED or UNSATURATED compound? (1)
4.2 Write down the TYPE of ADDITION reaction represented by:
4.2.1 Reaction 1 (1)
4.2.2 Reaction 2 (1)
4.3 For Reaction 1 write down the:
4.3.1 Name of the catalyst used (1)
4.3.2 Name or Formula of the inorganic reagent used (1)
4.4 For Reaction 3 write down:
4.4.1 ONE reaction condition (1)
4.4.2 Balanced equation using structural formulae for organic reagents (6)
[12]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a NEW page)
5.1 Consider the reaction represented by the balanced equation.
SnCℓ4(aq) + Br-(aq) SnCℓ2(aq) + Br2(ℓ)
5.1.1 Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer. (2)
5.1.2 Write down the oxidation number of the underlined substance in the equation. (1)
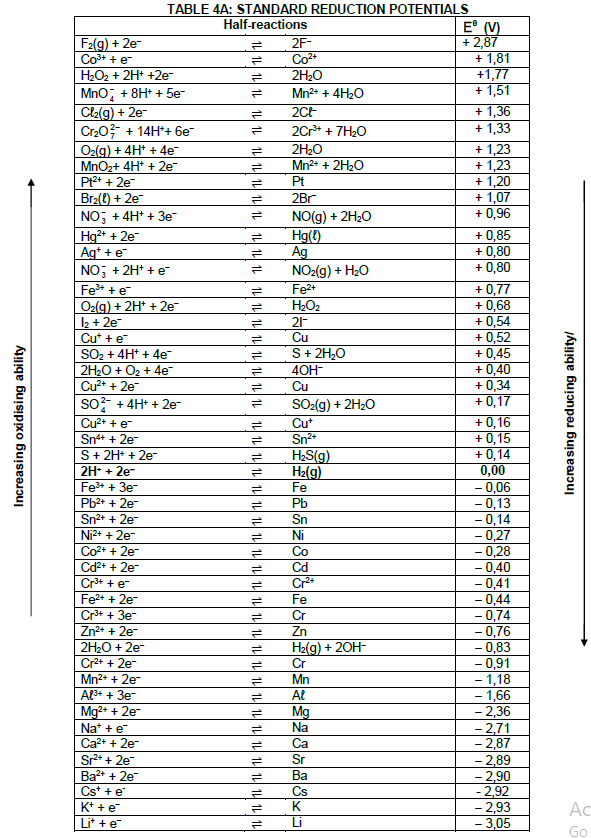
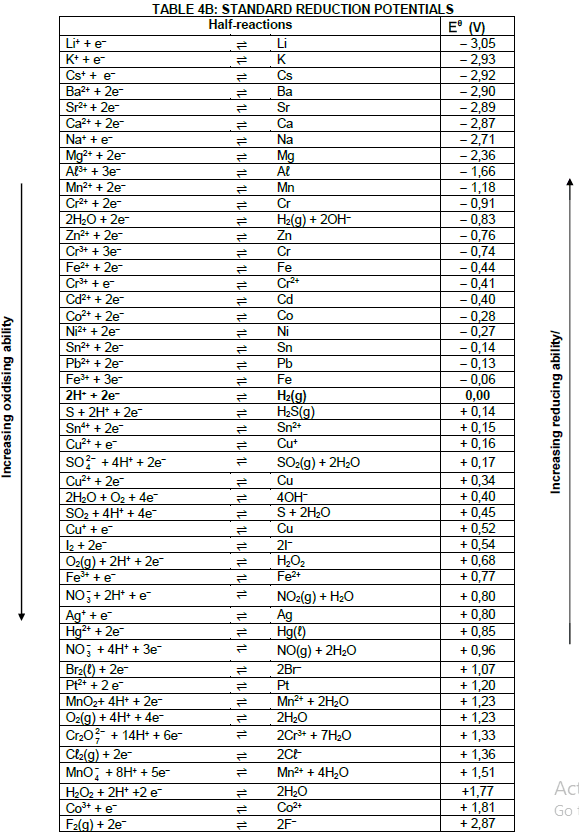
5.1.3 Determine by calculation whether the reaction is spontaneous. (5)
5.2 The following reactions occur spontaneously in galvanic cells P, Q, R and S.
| CELL | NET CELL REACTION |
| P | Ni + Au3+ Ni2+ + Au |
| Q | Mn + Ni2+ Mn2+ + Ni |
| R | Aℓ + Mn2+ Aℓ3+ + Mn |
| S | Aℓ + Au3+ Au + Aℓ3+ |
Which cell (P, Q, R or S) will produce the HIGHEST EMF?
Explain the answer without performing any calculation. (3)
5.3 Another galvanic cell, T, is constructed using Ni/ Ni2+ and Aℓ/ Al3+ half-cells.
For cell T.
5.3.1 Which electrode is the anode (Ni or Aℓ)? (1)
5.3.2 Write down the balanced overall ionic equation for the reaction that takes place. (3)
5.4 The diagram given below shows a galvanic cell constructed under standard conditions.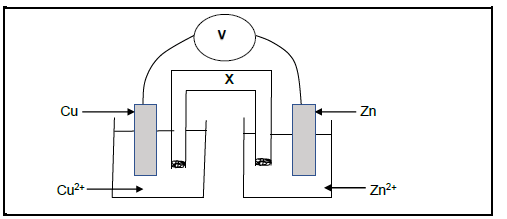
Write down the:
5.4.1 Energy change taking place when the cell is in operation (2)
5.4.2 TWO standard conditions for this cell (2)
5.4.3 TWO functions of component X (2)
5.4.4 Cell notation (3)
5.5 Fuel cells and biodiesel can be used as alternative energy sources to petrol or petroleum diesel.
Write down ONE:
5.5.1 Advantage of using biodiesel in place of petrol (1)
5.5.2 Disadvantage of using biodiesel in cars (1)
[26]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a NEW page)
Consider the electrochemical cell used for the electrolysis of copper (II) chloride solution below.
Graphite rods are used as electrodes.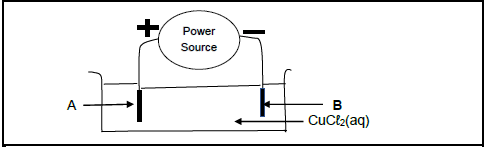
6.1 Define the term electrolysis. (2)
6.2 Is the power source AC or DC? (1)
6.3 In which direction will Cu2+ ions move in the solution?
Write down only TOWARDS A or TOWARDS B. (1)
6.4 Give a reason why copper (II) chloride crystals must be dissolved into the solution before electrolysis. (2)
6.5 Write down:
6.5.1 ONE observable change at electrode A (1)
6.5.2 The NAME or FORMULA of the oxidising agent (1)
6.6 Write down the half reaction taking place at electrode B. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a NEW page)
The diagrams given below (A and B) show TWO phenomena that can take place when a ray of light strikes a glass prism.
Study the ray diagrams and answer the questions that follow.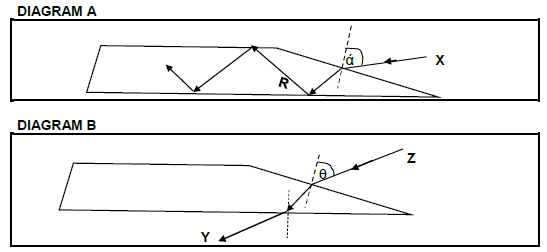
7.1 Define the term reflection. (2)
7.2 Write down the NAME of:
7.2.1 Ray X (1)
7.2.2 Ray R (1)
7.2.3 Ray Y (1)
7.2.4 Angle labelled θ in diagram B (1)
7.2.5 The phenomenon taking place inside the prism in diagram A (1)
7.2.6 The phenomenon shown in diagram B (1)
7.3 State TWO requirements for the phenomenon taking place inside the prism in diagram A. (2)
7.4 Is ray Z refracted AWAY or TOWARDS the normal as it travels inside the prism?
Give a reason. (3)
7.5 How does the angle θ in diagram B compare in size to the angle ά in diagram A?
Write only LARGER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO.
Explain the answer. (3)
[16]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a NEW page)
A group of learners investigate the effect of decreasing the distance between an object and a convex lens on the height of the image formed. They place the object at different positions from the lens as shown in the diagrams below and measure the height of the image formed at each position.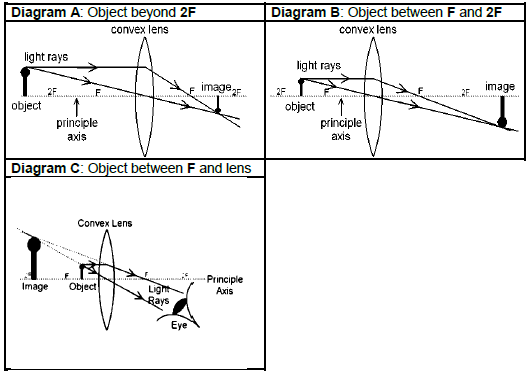
8.1 Besides the larger height of the image formed in diagram C, write down TWO other properties of the image formed in diagram C. (2)
8.2 For this investigation write down:
8.2.1 The independent variable (2)
8.2.2 TWO precautions that the learners must take to ensure a fair test (2)
The learners conclude that: “As the distance between the lens and the object decreases the height of the image increases.”
8.3 Is the learners’ conclusion generally TRUE? (YES or NO)
Explain the answer. (2)
8.4 In the diagram below the focal length (F) of the lens is 30 mm. Draw a ray diagram to determine the position of the image formed when an object of height 20 mm is placed at 2F. (4)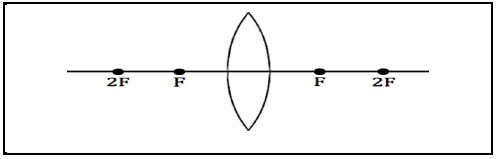
[12]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a NEW page)
9.1 The diagram below shows the spectrum obtained during the dispersion of white light.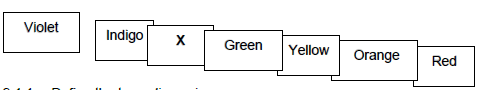
9.1.1 Define the term dispersion (2)
9.1.2 Write down the name of the colour of light represented by X. (1)
9.1.3 Which colour of visible light has the highest frequency? (1)
A photon of a light wave has 7,0 x 10-19 J of energy.
9.1.4 Define the term photon. (2)
9.1.5 Calculate the wavelength of the wave. (5)
9.2 An electromagnetic wave is defined below. Write down the missing word.
An electromagnetic wave is a changing … field and a changing magnetic field mutually perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation of the wave. (1)
9.3 Four of the seven electromagnetic radiations are listed below.
| Ultraviolet rays | Microwaves | Visible light | Infra-red rays |
Write down the NAME of electromagnetic radiation from the list given above that:
9.3.1 Is used in night-vision devices (1)
9.3.2 Leads to skin damage when one is over exposed to sunlight. (1)
9.3.3 Has photons with lowest energy (1)
9.4 Name THREE electromagnetic radiations NOT shown in the list given in QUESTION 9.3 above. (3)
[18]
TOTAL: 150
4.3 INFORMATION SHEETS – PAPER 2
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
| NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
| Standard pressure | pθ | 1,01 x 105 Pa |
| Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
| Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m·s-1 |
| Planck's constant | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J·s |
TABLE 2: WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT
| WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT | |
| v = f λ | T = 1 f |
| Energy | E = hf |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
| Eθcell= Eθcathode - Eθanode Eθcell = Eθreduction - Eθoxidation Eθcell= Eθoxidising agent - Eθreducing agent |
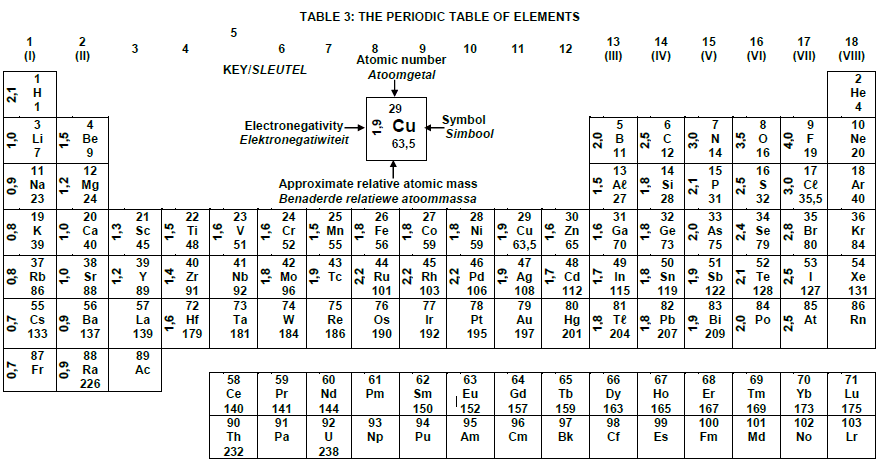
TABLE 3: THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS