TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
MEMORANDUM
SEPTEMBER 2018
QUESTION 1/VRAAG 1
1.1 D √√
1.2 C √√
1.3 A √√
1.4 A √√
1.5 C √√
1.6 A √√
1.7 B √√
1.8 C √√
1.9 C √√
1.10 D √√
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 2.1.1 A √ (or B) (1)
2.1.2 F √ (1)
2.1.3 A √ (1)
2.2 2.2.1 Alkyne √ (1)
2.2.2 Ester √ (1)
2.2.3 Alcohol √ (1)
2.3 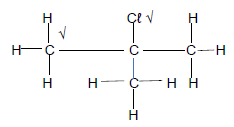
(2)
Marking criteria
|
2.4
2.4.1 Propanone √√ Accept propan-2-one OR 2-propanone (2)
2.4.2 3,4 √-dimethyl √ hexan-2-ol √ OR 3,4-dimethyl-2-butanol (3)
Marking criteria
|
2.5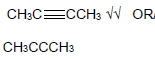
Marking criteria
|
2.6.1 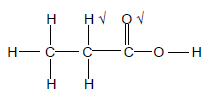
Marking criteria
|
2.6.2 Ethyl √ propanoate √ (2)
2.7 2.7.1 A molecule that contains a large number of atoms.√√ (2)
2.7.2 Plastics √ (1)
2.7.3 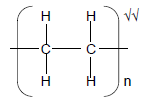
(2)
[24]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Resistance to flow. √√ (2)
3.2 C √ (1)
3.3 From A to C
Chain length/Surface area /Molecular size increases√
Strength of intermolecular forces (London forces/induced dipole forces) increases√
More energy needed to overcome intermolecular forces√ (3)
3.4 A √ (1)
3.5 Temperature at which vapour pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. √√ (2)
3.6 C5H12 + 8O2 √ 5CO2 + 6H2O √ bal √ (3)
[12]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Saturated √ (1)
4.2 4.2.1 Hydrogenation √ (1)
4.2.2 Hydrohalogenation √ (1)
4.3 4.3.1 Platinum/Palladium/Nickel √ (1)
4.3.2 Hydrogen √ / H2 (1)
4.4 4.4.1 Dilute base √ /Dilute KOH/NaOH/Add H2O/(Mild) Heat (1)
4.4.2 H 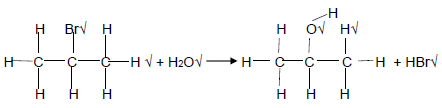
(6)
| MARKING CRITERIA Organic reactant Whole structure correct 2/2 Only functional group correct: 1/2 Organic product: Whole structure correct 2/2 Only functional group correct: 1/2 |
[12]
QUESTION 5
5.1 5.1.1 Loss of electrons √√ (2)
5.1.2 +4 √ (1)
5.1.3 Eocell = Eocathode-Eoanode √
= 0,15 √– 1.07 √
= -0.92V √
Not spontaneous Eocell is negative √ (5)
5.2 Cell S √
Aℓ is the strongest reducing agent√ and Au3+ is the strongest oxidizing agent √(3)
5.3 5.3.1 Aℓ √ (1)
5.3.2 2 Aℓ + 3 Ni2+ √ Aℓ3+ + Ni √ Bal √ (3)
5.4 5.4.1 Chemical energy changes to electrical energy √√ (2)
5.4.2 T = 25 oC √/298 K and c = 1 mol.dm-3 √ (2)
5.4.3 Completes the circuit √
Ensures electrical neutrality √ (2)
5.4.4 Zn/ Zn2+√ // Cu2+/Cu√
√ (3)
5.5 5.5.1 Less pollution/Renewable √ (1)
5.5.2 More expensive √ (1)
[26]
QUESTION 6
6.1 A process of breaking down a compound using electricity √√
OR
A process of using electrical energy to produce a chemical change √√ (2)
6.2 DC √ (1)
6.3 Towards/Na B √ (1)
6.4 To set ions free to move √√ (2)
6.5 6.5.1 Bubbles (of gas/chlorine) √ (1)
6.5.2 Cu2+ √ OR Copper(II) ion (1)
6.6 Cu2+ + 2e Cu √√ (2)
Marking criteria
- Cu ← Cu2+(aq) + 2e- (2/2) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Cu (1/2)
Cu ⇌ Cu2+(aq) + 2e- (0/2) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ← Cu (0/2) - Ignore if charge omitted on electron.
- If (+) charge omitted on Cu2+ Max.1/2
[10]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The change in direction of a wave upon striking the interface between two materials. √√ (2)
7.2 7.2.1 X Incident ray √ (1)
7.2.2 Y Emergent ray √ (1)
7.2.3 R Reflected ray √ (1)
7.2.4 Angle of incidence √ (1)
7.2.5 Total internal reflection√ (1)
7.2.6 Refraction√ (1)
7.3 Angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. √
Light must travel from a medium of higher optical density to a medium of lower optical density.√ (2)
7.4 Towards the normal / Na die normaal √
Light travels from a medium of lower optical density to a medium of higher optical density √√(3)
7.5 SMALLER THAN √
Total internal reflection occurs when angle of incidence is higher than the critical angle as in diagram 1 √√(3)
[16]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Upright √ (Erect)/ Virtual √(2)
8.2 8.2.1 Distance between the lens and object √√ (2)
8.2.2 Use the same lens √ / Use the same object √(2)
8.3 No√
When object is at 2F the size of the image is the same as that of object. √(2)
8.4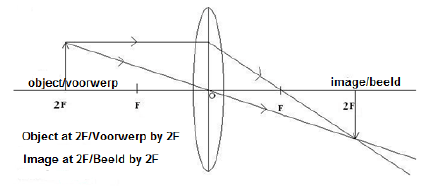
Marking criteria
|
[12]
QUESTION 9
9.1 9.1.1 The phenomenon whereby light breaks up into its component colours √√(2)
9.1.2 Blue √ (1)
9.1.3 Violet √ (1)
9.1.4 A quantum of energy √√ (2)
9.1.5 E = hf = hc/λ √ (Any one)
7 x 10-19 √ = 6.63 x 10-34 √ x 3x 108 √/ λ
∴ λ = 2,84 x 10 -7 m √ (5)
9.2 Electric √ (1)
9.3 9.3.1 Infra-red √ (1)
9.3.2 Ultra violet √ (1)
9.3.3 Microwaves √ (1)
9.4 Visible light√
Gamma rays √
Radio waves √ (3)
[18]
TOTAL: 150