LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guidelines will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts) A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners' assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
- Changes to the marking guidelines
No changes must be made to the marking guidelines without consulting the provincial internal moderator who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and the Umalusi moderators where necessary). - Official marking guidelines
Only marking guidelines bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education via the provinces must be used.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✓✓
1.1.2 A✓✓
1.1.3 C✓✓
1.1.4 A✓✓
1.1.5 C✓✓
1.1.6 D✓✓
1.1.7 C✓✓
1.1.8 B✓✓
1.1.9 B✓✓ (9 x 2) (18)
1.2
1.2.1 Endocrine✓
1.2.2 Monoculture✓
1.2.3 Spermatogenesis✓
1.2.4 Prolactin✓
1.2.5 Thorns✓
1.2.6 Carbon footprint✓
1.2.7 Tropism✓ (7)
1.3
1.3.1 Both A and B✓✓
1.3.2 A only✓✓
1.3.3 B only✓✓ (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1 Reflex arc✓ (1)
1.4.2
- B - Motor✓ neuron/multipolar neuron/efferent neuron (1)
- C - Interneuron✓/connector neuron (1)
- E - Sensory✓ neuron/unipolar neuron/afferent neuron (1)
1.4.3
- F✓ (1)
- A✓ (1)
1.4.4
- D✓ - Synapse✓ (2)
- G✓ - Myelin sheath✓ (2) (10)
1.5
1.5.1 Anaphase II✓ (1)
1.5.2
- Centriole✓ (1)
- Centromere✓ (1)
- Spindle fibre✓ (1)
1.5.3 The chromatids separate✓/centromere splits (1)
1.5.4 Crossing over✓ (1)
1.5.5 Reduces genetic variation✓ (1)
1.5.6
- Four✓/4 (1)
- 23✓ (1) (9)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Corpus luteum✓
- Placenta✓ (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
2.1.2 Progesterone levels are increasing✓ (1)
2.1.3
- High levels of progesterone✓
- inhibits/causes a decrease in the secretion of FSH✓ (2)
2.1.4 To prevent the growth of a new follicle✓/ovulation during the pregnancy (1)
2.1.5
- 39,5 – 21,6✓ = 17,9
17,9 × 100✓ = 82,87✓/82,9/83% (3)
21,6
2.1.6
-
- The endometrium/uterine lining/placenta will not be maintained✓
- Menstruation will begin✓/the placenta will detach/ she will have a miscarriage (2)
- Give the woman progesterone supplements✓ (1) (12)
2.2
2.2.1 Methane✓/CH4 (1)
2.2.2 Used as a fuel✓/cooking/heating/light/electricity
(Mark first ONE only) Any (1)
2.2.3
- Reduce pests✓/rats/flies
- Reduce bad smells✓/pollution
- To promote decomposition✓
(Mark first ONE only) Any (1)
2.2.4 It is full✓/It has reached ground level
(Mark first ONE only) (1)
2.2.5
-
- Golf course✓
- Recreational park✓
- Car park✓
- Forestry✓
(Mark first TWO only) Any (2)
-
- Reuse✓ waste materials
- Recycle✓ waste materials
- Reduce the amount of waste produced✓
- Manufacture more products that can be recycled✓
(Mark first TWO only) Any (2) (8)
2.3
2.3.1
- Cerebellum✓ (1)
- Cerebrum✓ (1)
2.3.2 Organ of Corti✓ (1)
2.3.3
- The semi-circular canals/part A contain fluid✓ /endolymph which moves when the person moves✓
- There are cristae✓/receptors present which convert the stimulus to an impulse✓/are sensitive to the movement of the fluid
- The canals lie on three different planes✓ to detect movement in any direction✓
(Mark first TWO only) Any 2 x 2 (4) (7)
2.4
2.4.1
- Choroid✓ (1)
- Sclera✓ (1)
2.4.2
- The person cannot see✓/is blind in that eye/has no binocular vision
- because the impulses from the retina cannot be transmitted to the cerebrum✓ from one eye (2)
2.4.3
- The circular muscles of part A/the iris contract✓
- and the radial muscles relax✓
- making the pupil smaller✓/constricting the pupil
- so that less light enters the eye✓ (4)
2.4.4
-
- Accommodation will not occur✓
- The refractive power of the lens is low✓/lens cannot become more convex
- and light rays are not refracted/bent enough✓
- and would not be focussed onto the retina✓/would be focussed behind the retina/a clear image would not be formed on the retina
- Therefore the person cannot focus on objects that are closer than 6m✓/the person can only focus on distant objects
Any (4)
- Convex✓/biconvex (1) (13) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 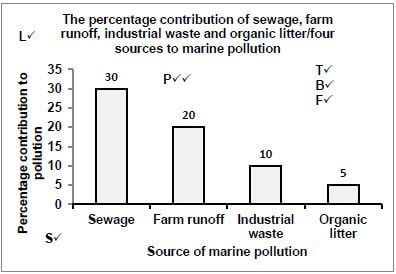
Mark allocation of the graph
Criteria | Mark Allocation |
Title of graph (T) including both variables | 1 |
Bar graph drawn (B) | 1 |
Correct scale for X-axis (equal width and spacing of the bars) and Y-axis (S) | 1 |
Correct label and unit for X-axis and Y axis (L) | 1 |
Only the correct four bars have been plotted (F) | 1 |
Plotting of the bars (P) | 0: No bars plotted correctly |
NOTE:
- If a line graph is drawn – marks will be awarded for the 'title and label for X and Y axes' only
- If a histogram is drawn – marks will be lost for the 'type of graph and correct scale' only (7)
3.1.2
- The sewage/organic litter contains nutrients✓
- The amount of nutrients in the water increases✓/eutrophication occurs
- causing an algal bloom✓
- The algae cover the surface of the water✓/blocks out sunlight
- causing water plants to die✓
- thereby reducing photosynthesis✓
- and increasing decomposition✓ thus reducing the oxygen content of the water Any (4) (11)
3.2
3.2.1 Adrenalin✓ (1)
3.2.2
- Increases the heart rate✓
- Increases blood pressure✓
- Stimulates the conversion of glycogen into glucose✓
- Increases the blood supply to the heart✓/skeletal muscles
- Decreases blood flow to the digestive system✓
- Decreases blood flow to the skin✓
- Increases muscle tone✓
- Increases the rate/depth of breathing✓
- Increases the rate of respiration✓/metabolism
- Dilates/increases the diameter of the pupils✓
(Mark first THREE only) Any (3) (4)
3.3
- Blood glucose levels rise✓ above normal
- The pancreas✓/islets of Langerhans
- secretes insulin✓ into the blood
- which travels to the liver✓/muscle cells
- and stimulates them to absorb glucose✓ from the blood
- and to convert the excess glucose into glycogen✓
- which decreases the blood glucose levels✓ to normal Any (5)
3.4
3.4.1
- Volume of urine✓ (1)
-
- Decide on a time✓/date/place to conduct the investigation
- Decide on the apparatus✓/materials that need to be used
- Decide how to record the data✓
- Decide on the number of participants to include✓
- Decide what factors to keep constant✓/example of factor to be kept constant
- Decide on the composition of the sample✓
- Develop an indemnity form for the participants to sign✓
- Recruit✓/get permission from volunteers to participate
(Mark first TWO only) Any (2)
-
- The same room✓/environment/temperature
- The same apparatus✓
- The same investigator✓
- No other liquid intake by both groups✓
- Same type of beer✓
(Mark first TWO only) Any (2)
-
- They used a large sample✓/12 men/6 men in each group
- The average volume of urine produced was calculated✓ (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
3.4.2
- Alcohol inhibits/reduces the secretion of ADH✓
- causing the renal tubules✓/distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
- to become less permeable to water✓
- Less water is reabsorbed✓ back into the blood
- A larger volume of urine is produced✓ Any (4) (11)
3.5
3.5.1 To ensure unilateral light✓/the plant receives light from one direction only (1)
3.5.2 Auxins✓/IAA/indole acetic acid (1)
3.5.3 Differences between plants A and B after two weeks
T✓
Plant A | Plant B |
The stem of the plant will bend towards the light✓ | The stem of the plant will remain straight✓/will not bend towards the light |
Does not have lateral branches✓/only lower lateral branches will start to grow | All the lateral branches will grow✓along the whole stem |
The plant will be taller✓ | The plant will be shorter✓ |
(Mark first TWO only) 1 table (T) + (2 x 2) (5)
3.5.4
- The gibberellins cause the stem/plant to grow longer✓/taller
- because gibberellins stimulate the elongation/growth of the internodes✓ (2) (9) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Gaseous exchange in amniotic eggs (A)
- Gases move by diffusion✓
- into and out of the egg✓
- through the porous shell✓/allantois/chorion
Nourishment of the embryo in amniotic eggs
- The egg contains yolk✓/albumin
- which provide nutrients✓ to the embryo Max (4)
Gaseous exchange and nourishment of the foetus in humans (F)
- In the placenta✓
- the mothers blood comes into close contact with the foetal blood✓
- Oxygen✓
- and nutrients✓
- diffuse from the mothers blood into the foetal blood✓
- in the umbilical veins✓
- This nutrient rich blood is carried to the foetus through the umbilical cord✓
- Carbon dioxide diffuses from the foetal blood✓
- in the umbilical artery✓
- into the maternal blood✓ Max (7)
Protection of the foetus in humans (P)
- The foetus develops inside the uterus✓
- and is protected by the mothers body✓
- Antibodies from the mothers blood✓
- pass into the foetus' blood and provide immunity✓
- The placenta acts as a microfilter✓
- preventing toxins from the mother entering the foetal blood✓
- The foetus is enclosed in the amnion✓
- which contains amniotic fluid✓
- The amniotic fluid provides protection against dehydration✓
- and acts as a shock absorber✓
- It provides a suitable temperature✓ for the developing embryo
Max (6)
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Relevance | Logical sequence | Comprehensive |
All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence | Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail |
All the information provided is relevant to:
There is no irrelevant information | All the information regarding the:
| At least the following points should be included:
|
1 mark | 1 mark | 1 mark |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150