ENDOCRINE SYSTEM GRADE 12 NOTES - LIFE SCIENCES STUDY GUIDES
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupENDOCRINE SYSTEM
LIFE SCIENCES
STUDY GUIDES AND NOTES
GRADE 12
CHAPTER 7: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
7.1 The human endocrine system
The endocrine system is responsible for chemical coordination and regulates activities that take place inside the body. The endocrine system consists of glands
that produce different hormones, which are the body’s chemical messengers. Figure 7.1 below shows the glands of the endocrine system, the hormones they produce and the function of these hormones in the body.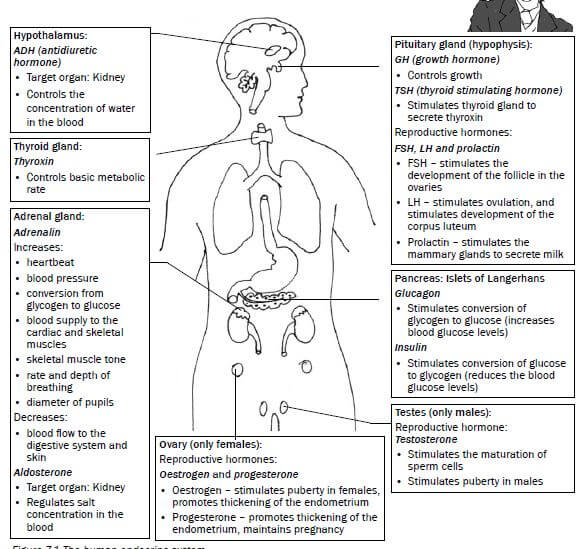
Figure 7.1 The human endocrine system
7.2 Negative feedback
Homeostasis is a process of maintaining a constant internal environment (blood and tissue fluid) within the body. This enables the body to function efficiently, despite changes in the external or internal environment.
Negative feedback mechanisms operate in the human body to detect changes or imbalances in the internal environment and to restore the balance.
7.2.1 General sequence of events in a negative feedback mechanism
Step 1: An imbalance is detected.
Step 2: A control centre is stimulated.
Step 3: Control centre responds.
Step 4: Message sent to target organ/s.
Step 5: The target organ responds.
Step 6: It opposes/reverses the imbalance.
Step 7: Balance is restored.
7.2.2 Example of a negative feedback mechanism
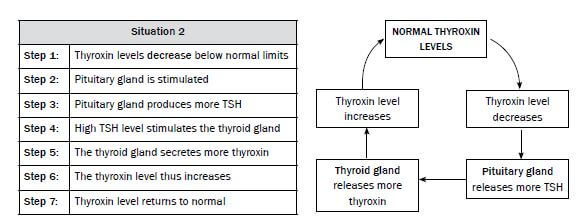
We will look at the regulation of thyroxin in the human body. There are two glands involved in the control of thyroxin levels:
- Gland 1: Thyroid gland (releases thyroxin)
- Gland 2: Pituitary gland (releases TSH)
Let us now look at the sequence of events in this feedback mechanism.
When you read the flow diagrams, start with NORMAL THYROXIN LEVELS.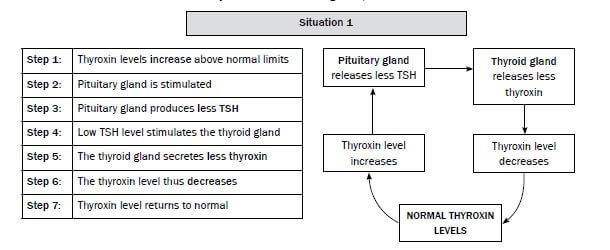
Activity 1
Question
The flow chart in Figure 7.2 below shows the control of glucose levels.
Provide labels for 1 to 6. [6]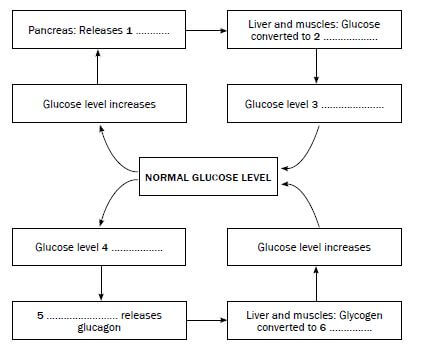
Figure 7.2 The negative feedback system to control glucose levels in the body
Answers to activity 1
- Insulin✔
- Glycogen ✔
- Decreases✔
- Decreases✔
- Pancreas ✔
- Glucose✔ [6]